Page 152 - WCS - Electrical
P. 152
WORKSHOP CALCULATION & SCIENCE - CITS
ii When gun fires a bullet, the force acts equally on the gun in opposite direction.
Unit of Force
In metric system, the unit of force is dyne and in Britishsystem, it is Poundal and in M.K.S. system, unit c of force
isnewton, i.e.
1 dyne force = Mass of 1 gram x Acceleration 1 cm/sec²
1 poundal force = Mass of 1 pound x Acceleration 1 foot/sec2
1 newton force = Mass of 1 kg x Acceleration 1 metre/sec²
= 10 dynes
5
1 gram weight = 980 dynes
1 pound weigh = 32 poundals
1 kg weight = 9.8 newton
To find out the resultant force
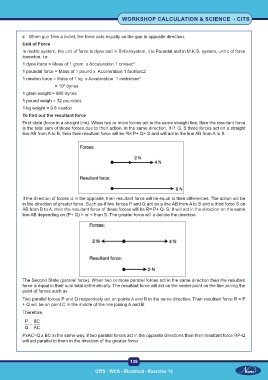
First state (force in a straight line). When two or more forces act in the same straight line, then the resultant force
is the total sum of those forces due to their action, in the same direction. If P, Q, S three forces act on a straight
line AB from A to B, then their resultant force will be R= P+ Q+ S and will act in the line AB from A to B.
If the direction of forces is in the opposite, then resultant force will be equal to their differences. The action will be
in the direction of greater force. Such as-If two forces P and Q act on a line AB from A to B and a third force S on
AB from B to A, then the resultant force of these forces will be R= P+ Q- S. It will act in the direction on the same
line AB depending on (P+ Q) > or < than S. The greater force will a decide the direction.
The Second State (parallel force). When two or more parallel forces act in the same direction then the resultant
force is equal to their sum total arithmetically. The resultant force will act on the center point on the line joining the
point of forces such as
Two parallel forces P and Q respectively act on points A and B in the same direction. Their resultant force R = P
+ Q will be on point C in the middle of the line joining A and B.
Therefore,
P = BC Q.Sin θ
Q AC tan α = P + Q.cos θ
PxAC=Q x BC In the same way, if two parallel forces act in the opposite directions then their resultant force RP-Q
BC
P
will act parallel to them in the direction of the greater force.
P× AC = Q× BC =
Q AC
Speed = Distance covered
QxBC Time
P =
AC 139
PxAC CITS : WCS - Electrical - Exercise 13
Definite
Distance
direction
P = Velocity =
BC Time
CD
Sin θ =
Q a = change in velocity m/sec 2
BD Time
Cos θ =
Q
1
2 2 2
R = P + Q + 2.P.Q cos θ
CD CD (v −u)
tan α = = F = m
OD OB + BD t
Q.Sin θ
=
P + Q.cos θ
Q.Sin θ
tan α =
P + Q.cos θ
2 2
R = P + Q + 2.P.Q cos θ