Page 156 - WCS - Electrical
P. 156
WORKSHOP CALCULATION & SCIENCE - CITS
2 Unstable Equilibrium.
If after a slight displacement a body does not regain its original position, it is called in unstable equilibrium e.g., a
cone standing on its vertex.
3 Neutral Equilibrium
If an object after a slight displacement does not return to its original position but its new state is like the old state
the object is said to be in a neutral state e.g., a cone placed on an inclined arm.
SOME EXAMPLES OF EQUILIBRIUM IN DAILY LIFE
1 The lower decks of the ships are loaded with heavy cargoes. This makes the centre of gravity of the whole ship
lower and its equilibrium becomes more stable.
2 A man carrying a bucket full of water in one hand extends his opposite arm and bends his body towards it.
3 While carrying load on back the man bends forward so that his and the load’s centre of gravity falls on his feet.
If he walks erect, he will fall backward.
4 While climbing a mountain, a man bends forward and bends backward while descending so that the
centre of gravity of his load falls on his feet.
5 In a double-decker bus, more passengers are accommodated in the lower deck and less on the upper so that
the centre of gravity of the bus and the passengers is kept low to eliminate any chance of turning
TYPES OF FORCES
Force is mainly classified as tensile force, compression force and shear force.
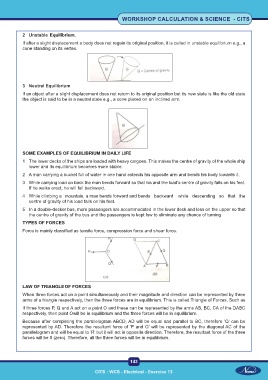
LAW OF TRIANGLE OF FORCES
When three forces act on a point simultaneously and their magnitude and direction can be represented by three
arms of a triangle respectively, then the three forces are in equilibrium. This is called Triangle of Forces. Such as
If three forces P, Q and A act on a point O and these can be represented by the arms AB, BC, CA of the DABC
respectively, then point Owill be in equilibrium and the three forces will be in equilibrium.
Because after completing the parallelogram ABCD, AD will be equal and parallel to BC, therefore ‘Q’ can be
represented by AD. Therefore the resultant force of ‘P and O’ will be represented by the diagonal AC of the
parallelogram and will be equal to ‘R’ but it will act in opposite direction. Therefore, the resultant force of the three
forces will be 0 (zero). Therefore, all the three forces will be in equilibrium.
143
CITS : WCS - Electrical - Exercise 13