Page 155 - WCS - Electrical
P. 155
BC
P
Q.Sin
=
α =
tan
AC
Q
θ
Q.cos
BC
BC
AC =
P×
P
BC
Q.Sin
θ
AC
=
Q
tan
α =
covered
Distance
AC
θ
Q.cos
P +
Speed =
QxBC
Time
P =
AC
=
BC
AC
Q
Distance
Definite
direction
PxAC
covered
Distance
P =
Speed =
Time
QxBC
P =BC
P
=
AC
tan
α =
Q
AC
Q.cos
θ
P +
CD
Sin
θ =
Definite
Distance
PxAC
P =
velocity
in
change
2
m/sec
a =
=
BC
Q×
P×
AC =
Cos Q× BC Q P = P× AC = Q Q× BC P P BC BC Velocity = P + Time θ Velocity = Q.Sin θ Time Time direction
BD
Q
AC
θ =
Q CD Speed = Distance covered
WORKSHOP CALCULATION & SCIENCE - CITS 1 change Time
θ =
Sin QxBC
P =
Q
in
velocity
2 2 AC a = m/sec 2
R = P + Q + 2.P.Q cos θ BD 2 Time
Cos
PxAC
Therefore =CD= Q sin ϴ as per Eq 1 θ = Q Velocity = Distance Definite direction
P =
Time
OB= P = CD = CD BC F = m (v −u) 1
tan
α
OD
BD
OB +
2
BD= Q cos ϴ as per Eq 2 QPR = θ = + CD 2 + 2.P.Q cos θ t 2
Sin
Therefore = Q.Sin θ Q a = change in velocity m/sec 2
CD
Time
P + Q.cos θ Cos α = BD = CD F = m (v −u)
tan
θ =
BD
OD
OB +
Q
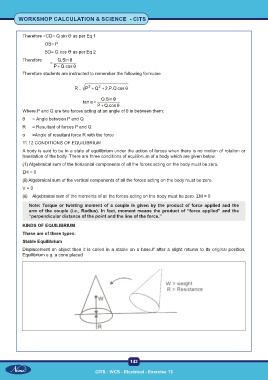
Therefore students are instructed to remember the following formulae t
Q.Sin θ
tan α = 1
P + Q.cos θ = Q.Sin θ
2
P + Q +
R = P + 2 Q.cos θ .Q cos θ 2
2.P
2 2 CD Q.Sin CD
θ
R = P + Q + 2.P.Q ta tan θ α = = F = m (v −u)
cos α n
=
P +
θ
OD Q.cos BD t
OB +
Where:P and Q are two forces acting at an angle of θ in between them:
θ = Angle between P and Q Q.Sin θ
= 2 2
R = P
P + Q.+
R = Resultant of forces P and Q Q + θ cos 2.P.Q cos θ
α =Angle of resultant force R with the force
θ
Q.Sin
α =
tan
P +
11.12 CONDITIONS OF EQUILIBRIUM Q.cos θ
A body is said to be in a state of equilibrium under the action of forces when there is no motion of rotation or
translation of the body. There are three conditions of equilibrium of a body which are given below:
2
2
cos
θ
2.P.Q
Q +
R =
P +
(1) Algebraical sum of the horizontal components of all the forces acting on the body must be zero.
ΣΗ = 0
(ii) Algebraical sum of the vertical components of all the forces acting on the body must be zero.
V = 0
(ii) Algebraical sum of the moments of all the forces acting on the body must be zero. ΣΜ = 0
Note: Torque or twisting moment of a couple is given by the product of force applied and the
arm of the couple (i.e., Radius). In fact, moment means the product of “force applied” and the
“perpendicular distance of the point and the line of the force.”
KINDS OF EQUILIBRIUM
These are of three types:
Stable Equilibrium
Displacement an object then it is called in a stable on a base.If after a slight returns to its original position,
Equilibrium e.g. a cone placed
142
CITS : WCS - Electrical - Exercise 13