Page 96 - WCS - Electrical
P. 96
Workshop Calculation & Science - Electronics Mechanic
Exercise 1.6.26
Exercise 1.6.26MechanicMechanic
Workshop Calculation & Science - Electronics MechanicWorkshop Calculation & Science - Electronics Workshop Calculation & Science - Electronics
Exercise 1.6.26
Workshop Calculation & Science - Electronics Mechanic
Trigonometry - Trigonometrical ratios
Exercise 1.6.26
Workshop Calculation & Science - Electronics Mechanic
Trigonometry - Trigonometrical ratiosTrigonometry - Trigonometrical ratiosTrigonometry - Trigonometrical ratios
Trigonometry - Trigonometrical ratios
Trigonometry - Trigonometrical ratios
Dependency
1
1
sec
θ
Dependency
DependencyDependency
1 1
1 AC
1
AC
1
AC
1
AB
AB
sec
θ θ
Dependency
cos sec
θ
θ
The sides of a triangle bear constant ratios for a given
1
1
AC
Dependency
θ AB
AB
cos
1 AB
θ
cos
AC
1 θ
AB AB
cos
AB θsec
The sides of a triangle bear constant ratios for a givenThe sides of a triangle bear constant ratios for a givenThe sides of a triangle bear constant ratios for a given
AC
definite value of the angle. That is, increase or decrease in
θ
sec
AB
AB
cos
θ
The sides of a triangle bear constant ratios for a given
AC
AB
AC
θ
AB
definite value of the angle. That is, increase or decrease indefinite value of the angle. That is, increase or decrease indefinite value of the angle. That is, increase or decrease in
The sides of a triangle bear constant ratios for a given
the length of the sides will not affect the ratio between them
AC
1
AB
definite value of the angle. That is, increase or decrease in
the length of the sides will not affect the ratio between themthe length of the sides will not affect the ratio between themthe length of the sides will not affect the ratio between them
AC
definite value of the angle. That is, increase or decrease in
unless the angle is changed. These ratios are trigonometrical
cot
θ
AB
1
1
1 AB
AB
1
1 1
Workshop Calculation & Science - Electronics MechanicWorkshop Calculation & Science
unless the angle is changed. These ratios are trigonometricalunless the angle is changed. These ratios are tri - Electronics
the length of the sides will not affect the ratio between them cotgonometricalunless the angle is changed. These ratios are trigonometrical Mechanic
tanθ θ cot Exercise 1.6.26Exercise 1.6.26
the length of the sides will not affect the ratio between them
BC
BC
θ
θ
cot
AB
ratios. For the given values of the angle a value of the ratios
1
1
BC
AB
BC BC
tanθ
1 BC
1
tanθ
unless the angle is changed. These ratios are trigonometrical
BC θ cot
AB
ratios. For the given values of the angle a value of the ratiosratios. For the given values of the angle a value of the ratiosratios. For the given values of the angle a value of the ratios
unless the angle is changed. These ratios are trigonometrical
θ
cot
BC
tanθ
BC
Trigonometry - Trigonometrical ratiosTrigonometry - Trigonometrical ratios
BC
AC
BC
ratios. For the given values of the angle a value of the ratios
AB
AB
AB
AB
BC
tanθ
BC
ratios. For the given values of the angle a value of the ratios
,
and
,
,
,
AB
ABAC
AC
ABBC
AC
sideBC AB
AC BCBC
BC
AC
BC
AB ABBC
ACAB
a
, AC
, AB
, AB
and ,,
and
,
and ACBC ,
BC ,,
,
,,
sin
AB
AB
BC
AB
AC
θ
AC
BC
do not change even whendo not change even whendo not change even when
asideBC
a
sideBC
sideBC
AB
BC AC
BC ACAB
ACAB
AC BCAC
AB BC and, AB
AC BCAB
BC
AB
BCAC
AB ,
AC BC,,
sin
sideAC θ sin
do not change even when
DependencyDependency
θ
b
1
AC
a 1 1
1
sideBC AC
the sides AB, BC, AC are increased to AB', BC' and AC' or
and
,
,
,
,
do not change even when
BC
AB
AC
AC
AB
BC
b
bsideAC
sideAC
b
sec
sideAC θ sin sec
a
sideBC θ
θ
AB
AC
the sides AB, BC, AC are increased to AB', BC' and AC' orthe sides AB, BC, AC are increased to AB', BC' and AC' orthe sides AB, BC, AC are increased to AB', BC' and AC' or
AB
BC
BC
AC
sin
decreased to AB", BC" and AC".
side AB
θ
c b θ AB
sideAC
cos
AB cosAB
AB
The sides of a triangle bear constant ratios for a givenThe sides of a triangle bear constant ratios for a given
the sides AB, BC, AC are increased to AB', BC' and AC' or
sideAC
cos
b
decreased to AB", BC" and AC".decreased to AB", BC" and AC".decreased to AB", BC" and AC".
the sides AB, BC, AC are increased to AB', BC' and AC' or
c
AB
side
side
AB
c side
c
AC
AC
For the anglealue of the angle. That is, increase or decrease in
definite value of the angle. That is, increase or decrease indefinite v
θ
cos
cos
decreased to AB", BC" and AC".
θ
b
sideAC θ cos
AB
side
c
decreased to AB", BC" and AC".
side b
b sideAC
sideAC
sideAC θ cos
For the angleFor the angle
For the angle
AB
c
the length of the sides will not affect the ratio between themthe length of the sides will not affect the ratio between them
θ
cos
AC is the hypotenuse
b
sideAC
1 1
1
1 AB
AB
For the angle
a
sideAC
b
For the angle
unless the angle is changed. These ratios are trigonometricalunless the angle is changed. These ratios are trigonometrical
cot
θ
cot
θ
AC is the hypotenuseAC is the hypotenuseAC is the hypotenuse
a
a
a
AB is the adjacent side
bBC
a
sin
BC BC
tanθ
θ BC
a tanθ
AC is the hypotenuse
b
ratios. For the given values of the angle a value of the ratiosratios. For the given values of the angle a value of the ratios
AC is the hypotenuse
a a
b
a
a θ
a a
sin
sin
AB is the adjacent sideAB is the adjacent sideAB is the adjacent side
θ
b
a x θ sin
b
b
b
a AB
AB
x c
x
x
c a
BC is the opposite side.
cos
c b
θ θ
AB is the adjacent side
b a
sin
b
BC
AB
AB
BC
AC
AB is the adjacent side ACABABBCAC BC
AC
sin
a
b
θ c
c c
c xθ
c
c b
cos
bc cos
bθ
b
BC is the opposite side.BC is the opposite side.BC is the opposite side.
c
a c cos
θ
,,
and ,,
,
,,
and
,
do not change even whendo not change even when
x
b c asideBC
a
sideBC
BC is the opposite side.
b
θ
c
AB
AB
The ratios BCACAB AB
BCAC
AC BCAC
BC
θ
sin
sin
c θ
c
BC is the opposite side.
b
θ
b
c b
cos b
The ratiosThe ratios
The ratios
b sideAC
sideAC
b
the sides AB, BC, AC are increased to AB', BC' and AC' orthe sides AB, BC, AC are increased to AB', BC' and AC' or
b
The ratios
BC
b side
The ratios
θ
tan
=
decreased to AB", BC" and AC".decreased to AB", BC" and AC".
BC side
side
BC
BC AB side
side side
c
c AB
tan AB
side
tan
tan
θ
θ
cos
=
cos
θ
θ =
BC
side
AB
BC
side sideAC
side
b
bsideAC
AB
tan side
θ AB side
For the angleFor the angle
=
tan
θ
=
1 AB
side
AB
side
or
or
cosec
1
θ
sin
θ
θ
θ.cosec
sin
AC is the hypotenuseAC is the hypotenuse AC do not change even when θ = θ cos θ AC AC sec cos c 1 sin AB AB θ sin 1 θ tanθ BC a b b θ Exercise 1.6.26Exercise 1.6.26
1
11
1
1
1
or cosec a
a
θ
sincosec
θ
sin
θ.cosec θ cosec or
sin
sin
1 orθ
θ
θ
θ
1
cosec θ sin
θ θ.cosec
Workshop Calculation & Science - Electronics MechanicWorkshop Calculation & Science - Electronics Mechanic
oror
Exercise 1.6.26Exercise 1.6.26
1
θ.cosec sin or
1
sin
1 θ
θθ θ
or
1 b
θ.cosec
a
cosec
AB is the adjacent sideAB is the adjacent side sin sin θ θ a θ cosec 1 b or a or ba cosec 1 cosec θ sin sin θ θ θ sin
cosec θ sin sin
θ
b
cosec
θ
θ.cosec
sin
1
or
θ
sin
1 x
x
θ
1
Workshop Calculation & Science
Trigonometry - Trigonometrical ratiosTrigonometry - Trigonometrical ratios
θ
θ
cosec
or
. θ
c c
cos
sec
sec
or
θ cc
BC is the opposite side.BC is the opposite side. cos θ cosc - Electronics sin Mechanic θ 1 Exercise 1.6.26
cb
WORKSHOP CALCULATION & SCIENCE - CITS
θ b θ cos
1
1
1
1
1
1
sec θsec
cos
θ
orcos
sec θ or
or
. θ θ sec
cos
cos orθ
θ
θ θ cos
1
1
1 MechanicMechanic
Workshop Calculation & Science - Electronics Workshop Calculation & Science -
or Exercise 1.6.26Exercise 1.6.26
cos Electronics
The ratiosThe ratiosTrigonometry - Trigonometrical ratios b or cos sec cos or sec θ . θ 1 sec θ or 1 θ cos θ . θ sec cos or θ 1 . θ sec θ 1
sec b
cos
1 cos
θ
. θ θ
1 θ
θ θ
sec
θθ
cos
sec
sec
sec
or
cos
cos
θ
θ
DependencyDependency
1 θ
sec
1 θ
1
AC
11
1AC
cos
- Electronics Mechanic- Electronics Mechanic& Science - Electronics Mechanic
Workshop Calculation & Science Workshop Calculation & Science Workshop Calculation
sec
θ θ sec
θ
. θ
tan
cot
or
1
cot
tan
Trigonometry - Trigonometrical ratiosTrigonometry - Trigonometrical ratios sec θ θ tan tan or θ θ θ θ tanθ θ θ . θ θ cot 1 1 Exercise 1.6.26Exercise 1.6.26Exercise 1.6.26
1
1
1
1 BC
1 side
BC side
cot 1 or θ AB
cos
AB AB
tan θ cos
cot θ AB
cot
Dependency
or
tan
1
. θ
The sides of a triangle bear constant ratios for a givenThe sides of a triangle bear constant ratios for a given
cot
θ
tanor
θ
or
θ
θ or
.
tan
1 θ
θ
cot
θ
1 cot
=
1
1 =
or tan tanAC
tan cot sec
θ MechanicMechanic
Workshop Calculation & Science - Workshop Calculation & Science
Electronics Electronics
side
θ -
1 θ
θθ cot
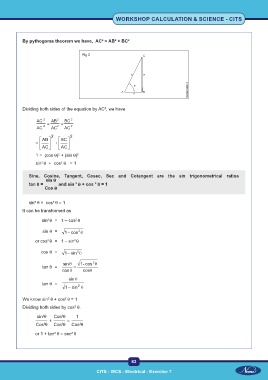
By pythogoras theorem we have, AC² = AB² + BC² 2 1 θ tan . θ cot or cot
. θ Exercise 1.6.26Exercise 1.6.26
tan
tan
θ
θ
or
θθ
cot tan
Trigonometry - Trigonometrical ratiosTrigonometry - Trigonometrical ratiosTrigonometry - Trigonometrical ratios cot AB θ AB θ or AB cos 2 θ θ = AB + BC 2
1 AB side AC
AC
tan By pythogoras theorem we have, AC
definite value of the angle. That is, increase or decrease indefinite value of the angle. That is, increase or decrease in
tan
or
cot
1
θ
θ
cot
tan
The sides of a triangle bear constant ratios for a given
DependencyDependency By pythogoras theorem we have, AC = AB + BCBy pythogoras theorem we have, AC = AB + BCBy pythogoras theorem we have, AC = AB + BC 2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
1
cot AC
1
θ
1 AC
tan 1
θ
the length of the sides will not affect the ratio between themthe length of the sides will not affect the ratio between them
1 AC
θ
θ
sec
1 sec
By pythogoras theorem we have, AC = AB + BC
definite value of the angle. That is, increas
1AB
11
The six ratios between the sides have precise definitions.e or decrease in AB AB 1 θ cosec AB or θ 1 sin 1 2 2 2 θ θ.cosec 2 1 2 θ 1
2
Trigonometry - Trigonometrical ratiosTrigonometry - Trigonometrical ratios
θ.cosec sin or
sin
θ
or
cosec or
θ
sin
By pythogoras theorem we have, AC = AB + BC
unless the angle is changed. These ratios are trigonometricalunless the angle is changed. These ratios are trigonometrical AB
θ cosAB
DependencyDependencyDependency
θ cot
cot
AC
θ 1 1
1 1 AC
1 AC
The sides of a triangle bear constant ratios for a givenThe sides of a triangle bear constant ratios for a given
The six ratios between the sides have precise definitions.The six ratios between the sides have precise definitions.The six ratios between the sides have precise definitions. θcosec θ tanθ BC cos θ sin θ 1
θ
sin
cosec
the length of the sides will not affect the ratio between them
sec
BC θ
BC BC θsec
θ sec
tanθ
The six ratios between the sides have precise definitions.
ratios. For the given values of the angle a value of the ratiosratios. For the given values of the angle a value of the ratios
AC
AB
Opposite
side
BC
definite value of the angle. That is, increase or decrease indefinite value of the angle. That is, increase or decrease in
AB
cos
The six ratios between the sides have precise definitions. AB AC cot AB θ θ cos ABAB 1 θ AB 1 cos θ
unless the angle is changed. These ratios are trigonometrical
SineThe sides of a triangle bear constant ratios for a givenThe sides of a triangle bear constant ratios for a given
The sides of a triangle bear constant ratios for a given
Sin
AB
BC θ
DependencyDependency
AB
θ side Opposite
OppositeBC
side BC
Opposite
side
1
1 AC
1
1
BC
1 BC
the length of the sides will not affect the ratio between themthe length of the sides will not affect the ratio between them
θ BC
Sine definite value of the angle. That is, increase or decrease indefinite value of the angle. That is, increase or decrease indefinite value of the angle. That is, increase or decrease in sec AC sec 1AC θ or 11 1 AC . θ sec cos or tanθ θ 1 . θ sec θ 1
θ
θ AB
Sin
AC
Sin
θ side θ
BCBC ratios. For the given values of the angle a value of the ratios θsec
Sin
ACSineABAB BCAC
cos
cos
AC
θ sec or θ
θ
AC
cos
Sine ACAB
Hypotenuse
BC
θ θ
or
Opposite
1 AB
1 1
AB
,
,
,
,
BC ,,
Opposite and,,
and
θ θ cos AB
AB
θ
sec
Sine
cos
AB
sec
Sin
cot
unless the angl BC ACAB AC BC side do not change even whendo not change even when θ sideBC θ cot AB θ asideBC a cos AB θ cos θ
Hypotenuse AC
θ
AC θ e is changed. These ratios are trigonometricalunless the angle is changed. These ratios are trigonometrical
HypotenuseHypotenuseAC
The sides of a triangle bear constant ratios for a givenThe sides of a triangle bear constant ratios for a given
AB
θ
SinBC
BCAC
the length of the sides will not affect the ratio between themthe length of the sides will not affect the ratio between themthe length of the sides will not affect the ratio between them
θ ACAB AB
Sine
sin BC
tanθ BC
θ BC
Hypotenuse ABABBCAC
AC
AC BC
1 AB AC
1 1
1 1 ABAC
AB
ratios. For the given values of the angle a value of the ratiosratios. For the given values of the angle a value of the ratios sin θ BC sideAC sideAC b tanθ 1
definite value of the angle. That is, increase or decrease indefinite value of the angle. That is, increase or decrease in
AC AB
,
b
and
Hypotenuse side Adjacent ,,,
the sides AB, BC, AC are increased to AB', BC' and AC' orthe sides AB, BC, AC are increased to AB', BC' and AC' or θ cotlunless the angle is changed. These ratios are trigonometrica
unless the angle is changed. These ratios are trigonometricalunless the angle is changed. These ratios are trigonometrica 1 cotl θ 1 θ cot 1 sideBC 1 a
do not change even when
AB
AB
Cosine
AB θ AB
CosBC
AB
AC
θ side Adjacent
side AB BCAC
Adjacent
AdjacentAB
θ BC
cot BC
tanθ
θ or θ sin tanθBC
cot
or BC
BC
side tan
1 . θ
or θ
cot
tan
. θ
θ
the length of the sides will not affect the ratio between themthe length of the sides will not affect the ratio between them
BC
θ AC
ratios. For the given values of the angle a value of the ratiosratios. For the given values of the angle a value of the ratiosratios. For the given values of the angle a value of the ratios
BCBC
θ θ AC
ABAC
AB
Cosine ACAB ABBC
θ Cosine
θ
Cos
Cosine decreased to AB", BC" and AC".decreased to AB", BC" and AC". Cos θ θ cot θ side AB θ sidesideAC c BC tancot or 1 tanθ tan θ 1
Hypotenuse
AC
AB
θ b
Adjacent
tan c 1AB
Cos side
θ AB 11
cot AB
tan
,
,,
,
and
,
AB the sides AB, and,,,
side
do not change even whendo not change even when
AB
θ θ
cossideBC AB
unless the angle is changed. These ratios are trigonometricalunless the angle is changed. These ratios are trigonometrical
AdjacentBC, AC are increased to AB', BC' and AC' or θ cot
θ cos asideBC AB cot
AC θ
Cosine
HypotenuseHypotenuseAC
a
Hypotenuse AC
AC BCAC
Cosine ACAB AB
θ BCAB
AB For the angleFor the angle Hypotenuse ACAB ABBC BC Cos θ AC By pythogoras theorem we have, AC = AB + BCBy pythogoras theorem we have, AC = AB + BC 2
BCAC
θ
Cos
b BC
BC
b tanθBC
θ
sideAC sideAC
sin
tanθ
BC
θ
sin
AB
AC BC
AC AB ABBC ACBC
2
AB
AC
2
BC
2
2
BC AC
2
decreased to AB", BC" and AC".
ratios. For the given values of the angle a value of the ratiosratios. For the given values of the angle a value of the ratios
c
,
,
, ,
,
b
and
, ,
ACBC and,,
, ,
and ,
Hypotenuseside Opposite do not change even whendo not change even whendo not change even when
cos
the sides AB, BC, AC are increased to AB', BC' and AC' orthe sides AB, BC, AC are increased to AB', BC' and AC' or sideAC bsideAC side AB a
sideBC
θ sideBC
a sideBC
a AB
AB
AB
BCAC
Opposite BCAC ABAB
side BC BCAC
BC θ ACBCAC ABAB
Tangent
AB
Tan BC
BCAC
sin
side sin
OppositeBC
AC is the hypotenuseAC is the hypotenuse
θ
sin
θ side Opposite
θ
sideAC
b
θ
2
For the angle
The six ratios between the sides have precise definitions.The six ratios between the sides have precise definitions. Dividing both sides of the equation by AC , we have 2 2
AB
AC
AC
AB
BC
BC
decreased to AB", BC" and AC".decreased to AB", BC" and AC". ACABABBCACBC
a
a
θ Tangent
side
Tan
Adjacent
θ θ
θ
AB
θ
Tangent
Tangent
c
c b side
AB sideAC
2 b
AB bsideAC
BC
Tan side
θ side
Opposite
Tan sideAC
Dividing both sides of the equation by AC , we haveDividing both sides of the equation by AC , we haveDividing both sides of the equation by AC , we have
and
,
, ,
,
, ,
,
and,
the sides AB, BC, AC are increased to AB', BC' and AC' orthe sides AB, BC, AC are increased to AB', BC' and AC' orthe sides AB, BC, AC are increased to AB', BC' and AC' or
side do not change even whendo not change even when
BC
cos
θ
cos
a
θ sideBC sideBC
a
2 θ
sin
sin
a
AB is the adjacent sideAB is the adjacent side
Tan
Adjacent
a θ
AB θ
2 b
aa
Tangent
b
2th sides of the equation by AC
Dividing both sides of the equation by AC², we have , we have
AC is the hypotenuse
AC
BC
AB AB
2
AB
AC AB
side AB BCAC BC
side
sin
a b
b
b sideAC
Tan
θ
sideAC sin
θ OppositeOppositeBC
BC
Tangent
Dividing bo b
side
θ
θ
For the angleFor the angle Opposite AC AdjacentAB BC θ side Adjacent side Dividing both sides of the equation by AC , we have
AC
decreased to AB", BC" and AC".decreased to AB", BC" and AC".decreased to AB", BC" and AC".
2
AB
side
Adjacent
c
x c AB
side
side
BC x c ABside
AB AB
2 sideAC sideAC
Sine θ Sine θ Adjacent Sin Cosec θ AC 2 cos 2 θ 2 θ = BC cθ cos + 2 cos b cb 2 BCAB cca 2 b b 2 a 2
side θ
Sin
θ
AB AC
Hypotenuse
2
the sides AB, BC, AC are increased to AB', BC' and AC' orthe sides AB, BC, AC are increased to AB', BC' and AC' or
c c
BC
2 AB AC θ
BC is the opposite side.BC is the opposite side.
AB cos
2 θ
θ AB is the adjacent side
2 AC b θ cos sin
Cosecant
AC
HypotenuseHypotenuseAC
Hypotenuse
HypotenuseHypotenuseAC
AC
AC is the hypotenuseAC is the hypotenuse
b bsideAC
ACbsideAC
AC
AC
2
2
For the angleFor the angleFor the angle
AC
2 2 AB
2
2
2 a
AC Cosec a
Cosecant decreased to AB", BC" and AC".decreased to AB", BC" and AC". Cosec = AC + sideAC + AC 2 BC = b ACAC ABside + = 2 x 2 + b AC 2
Opposite
Cosec θ
AB θ
side
BC
Cosecant Cosecant
2
ACAC c
θ
c
θ
2 2
θ
BC ABside
θ
AC
Hypotenuse
AC b
AC
=
AC
c
BC is the opposite side.
+ cos
ACos
cos θ
The ratiosThe rati
Hypotenuse
2
θ
2
BC
side BC
Opposite
Cosec side Opposite
Cosecant
a
AC ab
sin
sin
b
AB is the adjacent sideAB is the adjacent side side side OppositeBC θ θ side AC 2 AC θ =cos θ 2 2 AC a θ AC x a 2 θ a b x a b b c c
AC is the hypotenuseAC is the hypotenuseAC is the hypotenuse
b
2 2 b
Cosecant
Cosec
sideAC sideAC
For the angleFor the angle
θ
AdjacentAB
side
a
AB
Adjacent
Opposite
BC
AC
2 ⎡
2 ⎡
Hypotenuse
AC
2
b
22
BC
Cos
θ The ratios
θ
Cosine θ Cosine θ Opposite side HypotenuseHypotenuseAC θ Cos θ ⎡ AB⎤ sin ⎡ θ AB⎤ c cosθ sin b a θ BC⎤ BC side ⎡ AB cc b aa b BC⎤ a 2
+ side c
BC
BC is the opposite side.BC is the opposite side.
AB is the adjacent sideAB is the adjacent sideAB is the adjacent side
c
= θ
Secant
cos
b a θ
AB c ab sin
Sec
AC
Hypotenuse
AC
BC⎤ 2 b
⎢
=
⎥ =
BC⎤ ⎤ tan
⎥ 2⎤ tan
AC
HypotenuseHypotenuseAC
+ AC
side
Adjacent
=
θ θ
AB Secant
Secant θ AC is the hypotenuseAC is the hypotenuse Sec ⎢ ⎥ Sec ⎡ ⎢ θ 2 ⎦ ⎤ ⎢ ⎡ side ⎡ b +=x ⎡ θ b + x ⎡ θ ⎥
Sec
= θ
θ Secant
⎣ AB
AC x a
2 ⎦ ⎤ side a
Hypotenuse
AC
⎣ BC AB
⎢
⎢ ⎢ AB
⎥
AC
Hypotenuse
side
⎥ b c
⎣ c c
Secant
side AB
b θ
AB θ
AC⎦ c
⎣
AC⎦ cos
Sec
AdjacentAB
AC⎦ ⎦ cb
BC is the opposite side.BC is the opposite side.BC is the opposite side.
⎣ c
BC⎤ AC⎦ ccb θ
Adjacent
The ratiosThe ratios AB Adjacent side side side Sec θ θ side Adjacent side = ⎡ = θ ⎣ sin + ⎥ θ ⎡ cos 2⎢ b ⎢ b c cos 2= b ⎣ AC ⎥ ⎥ BC a tan θ
AB⎤ AC⎦ +
b
b
⎥ aθ
⎣ sin
AB is the adjacent sideAB is the adjacent side
⎢
aa
θ
Secant
⎥ ⎦
⎥ ⎦
⎢ 1 = (cos θ ⎣
⎣
AB
AC
AC
AB
Adjacent OppositeBC
Adjacent
⎢) + (sin θ) x
side
BC
AB Opposite
1 side x
⎣
2 1
1
1
side
⎣
AC⎦ b
AC⎦ b
2 b
Cot
θ
Cotangent
BC c
TangentosThe rati θ θ e rat side AB Tan AdjacentABTan θ θ sideAdjacent Dividing both sides of the equation by AC , we haveDividing both sides of the equation by AC or sin θ.cosec θ 1
Adjacentios
θ TangentosTh
2
θ
The rati BC is the opposite side.BC is the opposite side.
or b θ
θ sin BC side θ
θ c cos
AB
c
θ cosec c
c
cosec or b
side sin cos
1 = (cos θ) + (sin θ)1 = (cos θ) + (sin θ)1 = (cos θ) + (sin θ) , we have 1θθ.cosec sin or side c
22 2
2 2
tan
θ
Cot =
sin θ + cos θ = 1
Opposite
2 + (sin θ)
BC
=
θ
1 = (cos θ) cosec
θ
θ
Cotangent θ AB Cotangent Cotangent side Cot θ 1 = (cos θ) + (sin θ) ABside 2 θ θ tan sin θ sin θ 1
2
2 cosec
Cot side
θ θ
2
2
Adjacent
side
AdjacentAB
side
AB
Adjacent
2 2 1
AB
side
AB
Adjacent
Cotangent
Cot
sin θ + cos θ = 1 sin θ + cos θ = 1sin θ + cos θ = 1 θcosec orθ sin side b
side
BC
2 BC side
2
The ratiosThe ratios
Cotangent BC θ θ Opposite BC Opposite BC side OppositeBC θ θ sideOpposite 2 side 2 2 AB AC = side b 2 2 BC θ tan = tan BC 2 tan θ or sin θ.cosec θ 1
Cot
2
2
2
BCAB =
AC
θ
side
1 θ
θ
sin
2 sin θ + cos θ = 1 1 cosec
2
1
21
Relationship between the rat side sin θ + cos θ = 1, Tangent, Cosec, Sec and
Oppositeios
side
+ = 1 ABside
AC
Sine, Cosine + 1 ABside
θ 1 AB
BC HypotenuseHypotenuseAC
1
=
2 θ
2 θ sec or
sec cos
cos
. θ or
Relationship between the ratiosRelationship between the ratiosRelationship between the ratios AC sin cos 2 θ cos 2 sec or BC AC θ θ cosec or BC θ or tan sin θ θ.cosec sin or θ 1 sec . θ θ θ.cosec 1 θ 1 θ 1
θ side
cosec side
Cosec
2
sin
or
orθ
θ
θ
2
θ Cosec
Cosecant Cosecant
θ
θ
Sine, Cosine, Tangent, Cosec, Sec andSine, Cosine, Tangent, Cosec, Sec andSine, Cosine, Tangent, Cosec, Sec and
θ
ACAC sec
cos
cos
ACAC θ
sec
Cotangent are the six trigonometrical ratios
θ
tan
cosec =
=
1een the ratios BC
θ cosec
1 sin
1 side Opposite
θ
θ
Relationship betw OppositeBC
sin
1 θ
AC
Sine, Cosine, Tangent, Cosec, Sec and
or 1
cos 1
θ 1
1
1
1
θ side
sec
cos
. θ
or
1
sec
AB
Relationship between the ratios side 1 Cotangent are the six trigonometrical ratiosCotangent are the six trigonometrical ratiosCotangent are the six trigonometrical ratios
side
θ
AB
Cosec
θ
Sine, Cosine, Tangent, Cosec, Sec and
1
θ sin
AC
1
orsin
cosec orθ
sin
orcosec
sin
θ
1 1
1
θ cosec
θ
θ.cosec sin orθ
θ or
1 AC
θ θ.cosec θ.cosec sin or
1
AC
1
θ
2
θ
1 θ
1 cos
2sec
BC
Cotangent are the six trigonometrical ratios
1
2 2 1
sin
BC
θ θ
θ
Cosec θ AC Cosec Cosec Sine, Cosine, Tangent, Cosec, Sec and Cotangent are the six trigonometrical ratios
θ
θ
1
θ
sin
Sin cosec cosec
2 sin
2 sinθ
θ
θ
1
cosec
⎡
BC⎤
1
⎡ θ 1
⎡AB 1
and sin θθ θθ θ + cos θ θ θ θ θ = 1 cot or θ cot or 1
BC⎤
AB⎤
AC HypotenuseHypotenuseAC
θ
⎡
1
Cotangent are the six trigonometrical ratios 1 θ tan . θ cot or θ cot orθ tan
tan . θ
sin θ = θ =
θ =
AC
θ or 1
Sin cos 1
1 θ
1
BC θ
orθ
θ
sec
sec
or
Sin cos or θ
cos
cos
+ =
Sec
θ
Secant θ BC θ sin AC BC BCBC sin θ BC θ sin θ tan θ = θ = ⎥ θ tan θ = θ = ⎤ tan θ + sec ⎢ cot + cos ² θ = θ = Sin sec . θ 1 θ or θ 1 . θ 1 θ.cosec 1 θ 1 2
Sec
=
Cosec θ Secant
= 1 tan
⎢
Cosec
and sin θθ θθ θ + cos θ θ θ θ θ = 1 and sin θθ θθ θ + cos θ θ θ θ θ = 1 and sin θθ θθ θ + cos θ θ θ θ θ = 1 1θθ.cosec sin orθcosec orθ sin
2 θ cosec or
θ
sin
1 sin
tan
cot
⎥ ⎥
2 θ θ
=
tan θ = θ =
2
θ =
2 2
and sin ² θ = θ = 1 θ cosθ
θ
⎢ ⎢ sec
Cos θ = tan θ = θ = cosθsec
Sin
side
AB
Adjacent
AdjacentAB
AC⎦
⎣
⎣
AC BC BC BC sin sin θ AC side AC tan θ = θ = By pythogoras theorem we have, AC = AB + BCBy pythogoras theorem we have, AC = AB + BC1 θsec . θ cos or sec orθ cos ⎥ Cos θ = Cos cos 1 . θ θ cot θ . tan 1 2
AC⎦ ⎦
1 1
⎣AC 1
1 sin
Sin ⎣ tan 1 θcosec cosec
2 θθ θθ θ + cos θ θ θ θ θ = 1 or θ cot or θ
BC
θ
2 θ
1 sin
and sin
2 2 θ
AC⎦ θ
2 2 θ
tan θ θ =
Cos θ = θ =
2
Cos = θ =
sec
2
cos
cos
cos
θ
θ
sec
θ
2 sec . θ or θ
1
or
or
θ
θ sec or
θ = =
θ θ =
and sin θθ θθ θ + cos θ θ θ θ θ = 1 θ tanθ cot
AC AC tan θ = θ = Cos + (sin θ) 1 θ cosθ Cos 2 sec θ cos cos θ
sec
sec
2 2 1 θ
1 θ
2 1
side
AB AdjacentAB Adjacent side 1 = (cos θ) + (sin θ)1 = (cos θ) θ or 1 1 tan or 1 61
1
1 . θ
θ
cot
By pythogoras theorem we have, AC = AB + BC
θ
CotangentCotangent θ Cot θ Cot θ tan θ tan orθ cot θ or sec cot θ or cot θ or . θ cos . θ or tan θ 1 sec . θ 1 2 θ 1 2 61 2 61
The six ratios between the sides have precise definitions.The six ratios between the sides have precise definitions. cos cos
θ sec or
61 θsec cos
θ
2 θ
2 cot
cot
side
sin + cos² θ + cos θ = 1 11
θ
BC OppositeBC Opposite side sin² θ + cos θ = 1sin = 1 sec 2 θ tan θ θ 1 cos tan 1 θ θ cos 1 θ 61
1 sec
2
2
2
tan
cot
2 θ cot
θ orθ
The six ratios between the sides have precise definitions.
By pythogoras theorem we have, AC = AB + BCBy pythogoras theorem we have, AC = AB + BC
BC OppositeOppositeBC side side sin θ + cos θ =1 orθ tan cot θ θ cottan θ tancot θ oror cotcot θ . θ θ tanor tan θ θ 2 1 tan . or 2 cot 61 2 1 θ . θ tan θ 2 1
Cosine of an angle= Sine of its complementary
2
θ θ
tan
cot
θ Sine
Sine
θ
Sin
It can be transformed as 1
Relationship between the ratiosRelationship between the ratios θ Sin θ It can be transformed as 1 1 1 angle
AC
side
Opposite
By pythogoras theorem we have, AC = AB + BCBy pythogoras theorem we have, AC = AB + BCBy pythogoras theorem we have, AC = AB + BC
tancot
HypotenuseHypotenuseAC BC
2
Sine, Cosine, Tangent, Cosec, Sec andSine, Cosine, Tangent, Cosec, Sec and 2
The six ratios between the sides have precise definitions.The six ratios between the sides have precise definitions. tan θ tan θ or cot θ or cot θ or cot . θ or 2 2 θ 1 tan . θ 2 2 θ 1 2 2 2
θ
cot
θ
tan
cot
θ
tan
θ
AC 1 AC Sine θ 1 Sin θ Cotangent are the six trigonometrical ratiosCotangent are the six trigonometrical ratios
1 1
sin θ = 1 – cos θ
2
2
Hypotenuse
Examples
Cosec θ Cosec AB AdjacentAdjacentAB AC side side side By pythogoras theorem we have, AC = AB + BCBy pythogoras theorem we have, AC = AB + BC 2
The six ratios between the sides have precise definitions.The six ratios between the sides have precise definitions.The six ratios between the sides have precise definitions.
sideOpposite
OppositeBC
θ BC
2 2
2
2 2
θ
Sine BC Sine sin θ BC sin θ Sin θ Cos Sin θ θ Cos θ Sin Sin 2 2 2 2
θ
θ Cosine
BC BC
θ
Cosine
and sin θθ θθ θ + cos θ θ θ θ θ = 1 and sin θθ θθ θ + cos θ θ θ θ θ = 1
tan θ = θ = tan θ = θ =
θ = =
θ = =
θ θ =
sin θ =
BC
sideBC
AC AC HypotenuseHypotenuseAC
side
OppositeOppositeBC
side
AC
Adjacent
Opposite
–
1
AC HypotenuseHypotenuseAC AB
The six ratios between the sides have precise definitions.The six ratios between the sides have precise definitions. θ θ = cos 2 0 1 0
side
Cosine θ Sine
Sine θ Sine θ θ Sin θ Sin θ Sin θ θ Cos Cos If sin 30 = 2 find the value of sin 60
Cos
Hypotenuse
HypotenuseHypotenuseAC
AC BC AdjacentAB AC side Hypotenuse or cos θ = 1 – sin θ
AC
AB BC
side
OppositeOppositeBC
2
2
OppositeOppositeBC side Adjacent
side side
Tan θ
Cosine Sine θ θ θ Sine θ θ Cos θ Sin side Tan θ θ Dividing both sides of the equation by AC , we haveDividing both sides of the equation by AC , we have
61
θ θ Cos Sin
θ Cosine
By applying pythagores theorem
TangentTangent
61 2
2
AC AC
AB
sideAB
AdjacentAB
side Opposite side Adjacent
AdjacentAdjacentAB BC
2
TangentCosine
θ
θ
θ
Cosine θ Cosine AB HypotenuseHypotenuseAC HypotenuseHypotenuseAC Adjacent side side side θ Cos Tan θ θ cos θ = 2 2Dividing both sides of the equation by AC , we have
Cos
θ
–
sin
Cos
1
BC = AC - AB
2
2
2 2
2 2
AC AC OppositeBC AdjacentAB HypotenuseHypotenuseACside Opposite Hypotenuse AC 2 AB AC BCAB BC 2
HypotenuseHypotenuseAC
AC
AB
side
Adjacent
Adjacent
AB
side side
side
BC
+
CosecantCosecant
θ
Tangent Cosine θ θ Cosine θ Tan Cosec Tan θ Cos θ Cosec θ Cos θ θ Dividin 2 = ACAC + = 2 2 2 - 1 AB 2 2 2 BC 2 2 2
θ
θ Tangent
θ
2 2
ACg both sides of the equation by AC , we haveDividing both
ACAC sides of the equation by AC , we have
cos AC
sin AC
AdjacentAB HypotenuseHypotenuseAC
Opposite
BC
side
AB BC AC Opposite AC side Hypotenuse side Opposite tan θ = = = +
OppositeBC
side
side
BC
sideAdjacent BC
side Opposite
cos
2
Tan
Cosecant Tangent
Tan
Tangent θ Tangent θ θ θ θ Tan θ Cosec θ θ 2 2th sides of the equationividing both sides oD 2 2 2 2 cos 2 2 AC by AC , we havef the equation by AC , we haveth sides of the equation by AC , we have
Dividing boD
ACividing bo
2
2
2
2 2
2
AC 2
side
AB AC
BCAB
Opposite
BC
Adjacent
side
AB BC HypotenuseHypotenuseAC sideAB side side side AC ⎡ = AB⎤ + = BC⎤ ⎤ + ⎡ BC
AC AdjacentAdjacentAB
⎡ AB
⎡
BC⎤
HypotenuseHypotenuseAC OppositeOppositeBC
AC
θ
θ Secant
Sec
+
Secant
=
θ Tangent
θ
Tangent
2
Cosecant Cosecant θ θ Cosec θ Tan θ Sec θ θ θ AC = 2 2 Dividing bothDivid ⎥ ⎥ sides of the equation by AC , we haveing both sides of the equation by AC , we have
θ Cosec Tan
2
sin 2
⎥
2
+ 2
⎥
⎢ ⎢ACAC
2
2
⎢ 2 AC
⎢ ACAC
2 2
2 2
2 2
2 2 2
BCAB AC
AB AC
Adjacent
AdjacentAB
side
AB
AC
⎣
⎡
AC⎦ BC⎤
⎣
⎣ AC
⎡
sideOpposite
BC AB AC side Hypotenuse AC tan θ = ⎦ + = AC⎦ ⎦ AB⎤ ⎣ BCAB + BC
OppositeBC AdjacentAdjacentAB
ACside
side side
2+ =
=
HypotenuseHypotenuseAC
AC
Hypotenuse
1
θ
Secant
θ
θ Cosec
Cosecant Cosecant θ Cosecant θ Adjacent side side Sec θ AC 1 = (cos θ) + (sin θ)1 = (cos θ) + (sin θ)⎦ 2 2
+ 2 2
⎢
– = 2
2
sin 2 2
Cosec
θ
θ Cosec
2 2
⎢
2 ⎥ACAC
2 ⎥ AC
2 ACAC
ACACAC
2
AB
Adjacent
AC⎦
side
2 2 2
AC
2 22 2 2
2
⎣ BC
AB AC
AC
⎣ BCAB
AdjacentABside OppositeBC
BC
AB OppositeBC
side side Opposite
⎡
⎡
AB⎤
⎡
HypotenuseHypotenuseAC
⎡ AB
AC
CotangentCotangent AC
θ HypotenuseHypotenuseAC
θ
Cot
θ
Secant CosecantCosecant θ Sec θ Cot θ We know sin θ + cos θ = 1 += 2 2 = BC⎤ ⎤ 2 2 + = BC⎤ + 2 2 BC = 2 - 1 2
+
θ
θ
θ Secant
Sec
2
2
2
⎢
Cosec
2 2
θ Cosec
= θ
θ
2 ⎥ 2
⎢
2 ⎥ 2 ⎢ ACAC
2 ⎥ 2 ⎢ ACAC
2 ⎥ 22 AC
BC
Opposite
side
sin + cos² θ + cos θ = 1
We know sin² θ + cos θ = 1sin = 1
2
AB AdjacentAB OppositeBC AC Opposite side side ⎣ AB AC ⎣ BC⎦ 1 = (cos θ) + (sin θ) 2
AB
sideAdjacent
AC
side
Adjacent
⎣BCAB
⎡ ⎡
⎡ ⎣ AB
⎡
BC⎤
AC⎦ ⎤
⎡
AC⎦ ⎤ ⎤
AC⎦ ⎤ ⎤
⎡
HypotenuseHypotenuseAC
Hypotenuse
side
side
BC
AC
OppositeBC
Cot
Cotangent
θ
Secant θ Secant θ Secant θ θ Sec θ Sec Dividing both sides by cos θ. += + 2 ⎥ ⎥ = 2 ⎢ ⎢ ⎥ ⎥ + = 4 - 1
θ
= θ
Sec
⎢
⎥
Opposite
BC
sin . 22
2⎢ ⎢ 2
side
2⎢ 2
AC⎦
AB
sideAB
⎣
⎣ ⎣
AC⎦
⎦
1 = (cos θ) + (sin θ)1 = (cos θ) + (sin θ) ACAC⎦
⎣
AdjacentAB
side
⎣
AC⎦ ⎦
⎣ AC
22
2
side
Adjacent
Relationship between the ratiosRelationship between the ratios side AdjacentAB Adjacent Adjacent side Dividing both sides by cos² θ + cos θ = 1 ⎥
AB
Sine, Cosine, Tangent, Cosec, Sec andSine, Cosine, Tangent, Cosec, Sec and
⎡
AB⎤
⎡
BC⎤
⎡
BC⎤ ⎤
HypotenuseHypotenuseAC
AC
θ
Cotangent Cotangent θ Opposite Cot side θ Cot θ 2 θ 2 = ⎢ 2 2 ⎥ = 1 ⎢ ⎢ ⎡ AB 22 ⎥ ⎥ + ⎢ 2 2 ⎥ = 3
θ
θ Secant
Sec
Sec
+
Secant
θ
θ Cotangent are the six trigonometrical ratiosCotangent are the six trigonometrical ratios
side
BC
OppositeBC
cos
1 = (cos θ) + (sin θ) θ = 1 + (sin θ)
θ sin²θ + cos θ = 1sin
2
2
11
1 = (cos θ) 1 ACAC⎦
Adjacent
Adjacent
ABAB
Sine, Cosine, Tangent, Cosec, Sec and
1AC AdjacentAB
AC Relationship between the ratios AdjacentAB
AdjacentAB
⎣ AC
side
⎣
side
1 side
⎦ ⎦
⎣
AC⎦
side
=
+
Cosec θ Cosec CotangentCotangent θ side Cot θ Cot sin 2 sin 2 θ 2 + ⎣ Cos²θ + cos + (sin θ)1 = (cos θ) 2
θ
=
Cotangent
θ
θ
θ
Cot
2
cos
θ BC
Cotangent are the six trigonometrical ratios
BC =
sin
sin
cos
θ
θ
sideBC
Sin
side
Cos²θ + cos
sin
Cos²θ + cos θ = 1sin
BC BC
BC BC Opposite OppositeBC
2 θ = 1
2
AC
1
cos 2
1
2
Relationship between the ratiosRelationship between the ratios Opposite side θ Cos²θ + cos θ = 1sin 2 2 Sin 2 and sin θθ θθ θ + cos θ θ θ θ θ = 1 and sin θθ θθ θ + cos θ θ θ θ θ = 1 and
1 = (cos θ) + (sin θ)1 = (cos θ) + (sin θ)
2
2
2
2
AB
side
AdjacentAB
Adjacent
side
θ θ =
θ = =
2
Sine, Cosine, Cosine, Tangent, Cosec, Sec
tan θ = θ = tan θ = θ = Tangent, Cosec, Sec andSine,
2
2
θ = =
θ θ =
θ
Cosec
AC θ
CotangentCotangent AC θ BC Cot θ Cot θ 2 Cos Cos
θ
sin
2
Cotangent are the six trigonometrical ratiosCotangent are the six trigonometrical ratios
Sin
Relationship betwRelationship between the ratiosRelat BC BC OppositeBC Opposite side or 1 + tan θ = sec θ 22 tan θ = θ = Cosine, Tangent, Cosec, Sec and
side
or 1 + tan² θ + cos θ = 1sin
sin = sec² θ + cos θ = 1
1een the ratios 11ACionship between the ratios
1
2
2
AC
0 θ θ θ θ θ = 1
θ = =
and sin θθ θθ θ + cos
θ θ =
2
Sine, Cosine, Tangent, Cosec, Sec andSine, Cosine, Tangent, Cosec, Sec andSine,
2
AC
θ
Cosec θ Cosec θ BC sin θ Using the same equation Cos sin 60 =
BCBC
sin
Cotangent are the six trigonometrical ratiosCotangent are the six trigonometrical ratiosCotangent are the six trigonometrical ratios
BC
61
61
Sin
Sin
1 1 AC
1 AC
AC
Relationship between the ratiosRelationship between the ratios
θ θ =
θ θ =
θ = = Sine, Co
and sin θθ θθ
and sin θθ θθ θ + cos θ θ θ θ θ = 1θ + cos θ θ θ θ θ = 1
θ = =
2 2
2
2
Cosec θ Cosec Cosec 1 1 1 2 tan θ = θ = tan θ = θ = sine, Tangent, Cosec, Sec andSine, Cosine, Tangent, Cosec, Sec and
θ
θ
AC
AC
2
Cos
sin
BC AC sin θ BC BC 11 θ BC 1 sin θ sin θ + cos θ = 1. Cos 2 Sin 2 2 2 2 3 2 61
BC BC
Cotangent are the six trigonometrical ratiosCotangent are the six trigonometrical ratios
Sin
Sin
1AC
Cosθ
θ = =
θ θ =
θ θ =
θ θ =
θ = =
θ = =
Find the other trigonometrical ratios
tan θ = θ = tan θ = θ = tan θ = θ =
Cosec θ Cosec AC AC Dividing both sides by sin θ, and sin θθ θθ θ + cos θ θ θ θ θ = 1 and sin θθ θθ θ + cos θ θ θ θ θ = 1 and sin θθ θθ θ + cos θ θ θ θ θ = 1
AC θ
5
2
Cos
Cos
Cos
BC BC BC sin θ BC sin θ Sin Sin 61 61
θ θ =
θ θ =
θ = =
θ = =
2
2
2
83
2
2
AC AC cos tan θ = θ = tan θ = θ = and sin θθ θθ θ + cos θ θ θ θ θ = 1 and sin θθ θθ θ + cos θ θ θ θ θ = 1
By applying pythagores theorem
1
Cos Cos
1 = 61 61 61
2
sin sin 2 CITS : WCS - Electrical - Exercise 7
AB = AC - BC
2
2
2
61 61
1 + cot θ = cosec θ = 5 - 3 = 25 - 9
2
2
2
2
1 + tan θ = sec θ = 16
2
2
Trigonometrical Tables
Ratio 0 o 30 o 45 o 60 o 90 o
1 1 3
sin θ 0 1
2 2 2
AB = 16 = 4
3 1 1
cos θ 1 0
2 2 2 Now
1
tan θ 0 1 3 ∞
3
When θθ θθ θ increases,
Sine value increases;
Cosine value decreases;
Tangent value increases to more than 1 when the
angle is more than 45 (tan60 = 1.732)
o
o
Sine of an angle = Cosine of its complemen-
tary angle
st
62 WCS - Electronics Mechanic : (NSQF - Revised Syllabus 2022) - 1 Year : Exercise 1.6.26