Page 65 - CITS - WCS - Mechanical
P. 65
WORKSHOP SCIENCE - CITS
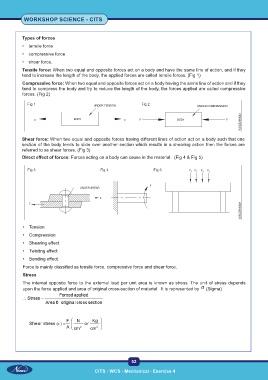
Types of forces
• tensile force
• compressive force
• shear force.
Tensile force: When two equal and opposite forces act on a body and have the same line of action, and if they
tend to increase the length of the body, the applied forces are called tensile forces. (Fig 1)
Compressive force: When two equal and opposite forces act on a body having the same line of action and if they
tend to compress the body and try to reduce the length of the body, the forces applied are called compressive
forces. (Fig 2)
Fig 1 Fig 2
Shear force: When two equal and opposite forces having different lines of action act on a body such that one
section of the body tends to slide over another section which results in a shearing action then the forces are
referred to as shear forces. (Fig 3)
Direct effect of forces: Forces acting on a body can cause in the material. (Fig 4 & Fig 5)
Fig 3 Fig 4 Fig 5
• Tension
• Compression
• Shearing effect
• Twisting effect
• Bending effect.
Force is mainly classified as tensile force, compressive force and shear force.
Stress
The internal opposite force to the external load per unit area is known as stress. The unit of stress depends
upon the force applied and area of original cross-section of material. It is represented by (Sigma)
F N Kg
Shear stress (τ ) = or
A cm 2 cm 2
52
CITS : WCS - Mechanical - Exercise 4