Page 66 - CITS - WCS - Mechanical
P. 66
WORKSHOP SCIENCE - CITS
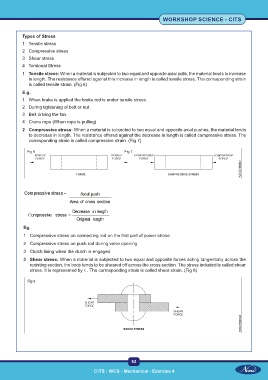
Types of Stress
1 Tensile stress
2 Compressive stress
3 Shear stress
4 Torsional Stress
1 Tensile stress: When a material is subjected to two equal and opposite axial pulls, the material tends to increase
in length. The resistance offered against this increase in length is called tensile stress. The corresponding strain
is called tensile strain. (Fig 6)
E.g.
1 When brake is applied the brake rod is under tensile stress.
2 During tightening of bolt or nut.
3 Belt driving the fan.
4 Crane rope (When rope is pulling)
2 Compressive stress: When a material is subjected to two equal and opposite axial pushes, the material tends
to decrease in length. The resistance offered against the decrease in length is called compressive stress. The
corresponding strain is called compressive strain. (Fig 7)
Fig 6 Fig 7
Axial push
Compressiv e stress =
Area of cross section
Decrease in length
C ompressive stress =
Original length
Eg.
1 Compressive stress on connecting rod on the first part of power stroke
2 Compressive stress on push rod during valve opening
3 Clutch lining when the clutch is engaged
3 Shear stress: When a material is subjected to two equal and opposite forces acting tangentially across the
resisting section, the body tends to be sheared off across the cross section. The stress included is called shear
stress. It is represented by τ . The corresponding strain is called shear strain. (Fig 8)
Fig 8
53
CITS : WCS - Mechanical - Exercise 4 CITS : WCS - Mechanical - Exercise 4