Page 151 - CITS - Welder - Trade Theory
P. 151
WELDER - CITS
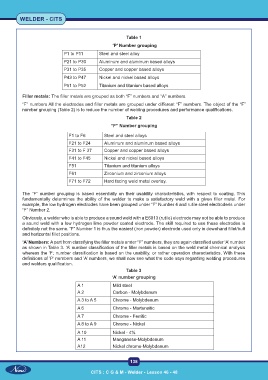
Table 1
‘P’ Number grouping
P1 to P11 Steel and steel alloy
P21 to P30 Aluminum and aluminum based alloys
P31 to P35 Copper and copper based alloys
P43 to P47 Nickel and nickel based alloys
P51 to P52 Titanium and titanium based alloys.
Filler metals: The filler metals are grouped as both “F” numbers and “A” numbers.
“F” numbers All the electrodes and filler metals are grouped under different “F” numbers. The object of the “F”
number grouping (Table 2) is to reduce the number of welding procedures and performance qualifications.
Table 2
“F” Number grouping
F1 to F6 Steel and steel alloys
F21 to F24 Aluminum and aluminum based alloys
F31 to F 37 Copper and copper based alloys
F41 to F45 Nickel and nickel based alloys
F51 Titanium and titanium alloys
F61 Zirconium and zirconium alloys
F71 to F72 Hard facing weld metal overlay.
The “F” number grouping is based essentially on their usability characteristics, with respect to coating. This
fundamentally determines the ability of the welder to make a satisfactory weld with a given filler metal. For
example, the low hydrogen electrodes have been grouped under “F” Number 4 and rutile steel electrode4s under
“F” Number 2.
Obviously, a welder who is able to produce a sound weld with a E6013 (rutile) electrode may not be able to produce
a sound weld with a low hydrogen lime powder coated electrode. The skill required to use these electrodes is
definitely not the same. “F” Number 1 is thus the easiest (iron powder) electrode used only in downhand fillet/butt
and horizontal fillet positions.
‘A’ Numbers: A part from classifying the filler metals under “F” numbers, they are again classified under ‘A’ number
as shown in Table 3. ‘A’ number classification of the filler metals is based on the weld metal chemical analysis
whereas the ‘F; number classification is based on the usability, or rather operation characteristics. With these
definitions of ‘P’ numbers and ‘A’ numbers, we shall now see what the code says regarding welding procedures
and welders qualification.
Table 3
‘A’ number grouping
A 1 Mild steel
A 2 Carbon - Molybdenum
A 3 to A 5 Chrome - Molybdenum
A 6 Chrome - Martensitic
A 7 Chrome - Ferritic
A 8 to A 9 Chrome - Nickel
A 10 Nickel - 4%
A 11 Manganese-Molybdenum
A12 Nickel chrome-Molybdenum
138
CITS : C G & M - Welder - Lesson 46 - 48