Page 44 - CITS - Computer Software Application -TT
P. 44
COMPUTER SOFTWARE APPLICATION - CITS
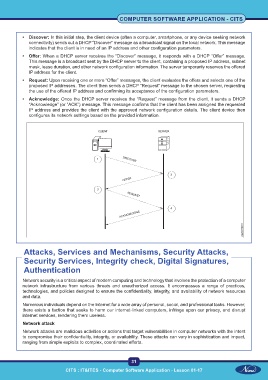
• Discover: In this initial step, the client device (often a computer, smartphone, or any device seeking network
connectivity) sends out a DHCP “Discover” message as a broadcast signal on the local network. This message
indicates that the client is in need of an IP address and other configuration parameters.
• Offer: When a DHCP server receives the “Discover” message, it responds with a DHCP “Offer” message.
This message is a broadcast sent by the DHCP server to the client, containing a proposed IP address, subnet
mask, lease duration, and other network configuration information. The server temporarily reserves the offered
IP address for the client.
• Request: Upon receiving one or more “Offer” messages, the client evaluates the offers and selects one of the
proposed IP addresses. The client then sends a DHCP “Request” message to the chosen server, requesting
the use of the offered IP address and confirming its acceptance of the configuration parameters.
• Acknowledge: Once the DHCP server receives the “Request” message from the client, it sends a DHCP
“Acknowledge” (or “ACK”) message. This message confirms that the client has been assigned the requested
IP address and provides the client with the approved network configuration details. The client device then
configures its network settings based on the provided information.
Attacks, Services and Mechanisms, Security Attacks,
Security Services, Integrity check, Digital Signatures,
Authentication
Network security is a critical aspect of modern computing and technology that involves the protection of a computer
network infrastructure from various threats and unauthorized access. It encompasses a range of practices,
technologies, and policies designed to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of network resources
and data.
Numerous individuals depend on the Internet for a wide array of personal, social, and professional tasks. However,
there exists a faction that seeks to harm our internet-linked computers, infringe upon our privacy, and disrupt
internet services, rendering them useless.
Network attack
Network attacks are malicious activities or actions that target vulnerabilities in computer networks with the intent
to compromise their confidentiality, integrity, or availability. These attacks can vary in sophistication and impact,
ranging from simple exploits to complex, coordinated efforts.
31
CITS : IT&ITES - Computer Software Application - Lesson 01-17