Page 80 - CITS - Computer Software Application -TT
P. 80
COMPUTER SOFTWARE APPLICATION - CITS
Designing Database using Normalization Rules
Normalization
Normalization is a database design process that involves organizing and structuring a relational database to
reduce data redundancy and dependency, thereby improving data integrity and overall efficiency. The primary
goal of normalization is to eliminate anomalies that can occur when data is stored in a non-optimal structure.
It helps ensure that the data is stored in a way that minimizes redundancy while preserving the relationships
between different pieces of information.
The process of normalization is typically carried out through a series of steps or “normal forms,” each addressing
specific types of data anomalies. The most commonly discussed normal forms are the first normal form (1NF),
second normal form (2NF), third normal form (3NF), and beyond.
Here’s a brief overview of these normal forms
1 First Normal Form (1NF)
In 1NF, each column in a table must hold only atomic (indivisible) values, and each row should be uniquely
identifiable. This eliminates the possibility of storing multiple values within a single cell and ensures that the
data is organized in a tabular format.
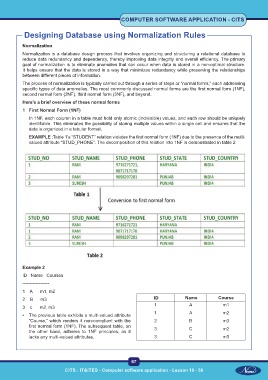
EXAMPLE :Table 1’s “STUDENT” relation violates the first normal form (1NF) due to the presence of the multi-
valued attribute “STUD_PHONE”. The decomposition of this relation into 1NF is demonstrated in table 2
Example 2
ID Name Courses
------------------
1 A m1, m2
2 B m3 ID Name Course
1 A m1
3 c m2, m3
• The previous table exhibits a multi-valued attribute 1 A m2
“Course,” which renders it non-compliant with the 2 B m3
first normal form (1NF). The subsequent table, on 3 C m2
the other hand, adheres to 1NF principles, as it
lacks any multi-valued attributes. 3 C m3
67
CITS : IT&ITES - Computer software application - Lesson 18 - 36