Page 83 - CITS - Computer Software Application -TT
P. 83
COMPUTER SOFTWARE APPLICATION - CITS
6 Hash Functions: Use cryptographic hash functions to create checksums or hashes of data. Comparing these
hashes can reveal any unauthorized changes to the data.
7 Data Verification: Periodically verify the accuracy and consistency of data through reconciliation and
verification processes.
8 Data Governance: Establish data governance policies and procedures to enforce data integrity standards
across the organization.
Types of data integrity
There are mainly four types of Data Integrity:
1 Domain Integrity
2 Entity Integrity
3 Referential Integrity
4 User-Defined Integrity
Domain Integrity
Domain, in this context, pertains to the acceptable values within a specified range. It denotes the scope of values
that can be utilized and stored in a specific database column. The available data types primarily include integers,
text, and dates, among others. It’s important that any input entered into a column falls within the permissible range
of the associated data type.
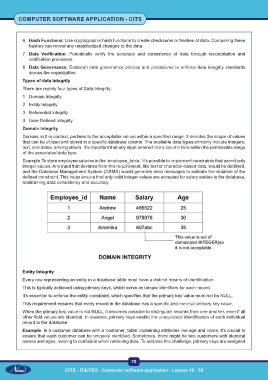
Example-To store employee salaries in the ‘employee_table,’ it’s possible to implement constraints that permit only
integer values. Any input that deviates from this requirement, like text or character-based data, would be declined,
and the Database Management System (DBMS) would generate error messages to indicate the violation of the
defined constraint. This helps ensure that only valid integer values are accepted for salary entries in the database,
maintaining data consistency and accuracy.
Entity Integrity
Every row representing an entity in a database table must have a distinct means of identification.
This is typically achieved using primary keys, which serve as unique identifiers for each record.
It’s essential to enforce the entity constraint, which specifies that the primary key value must not be NULL.
This requirement ensures that every record in the database has a specific and non-null primary key value.
When the primary key value is not NULL, it becomes possible to distinguish records from one another, even if all
other field values are identical. In essence, primary keys enable the unequivocal identification of each individual
record in the database.
Example: In a customer database with a ‘customer_table’ containing attributes like age and name, it’s crucial to
ensure that each customer can be uniquely identified. Sometimes, there might be two customers with identical
names and ages, leading to confusion when retrieving data. To address this challenge, primary keys are assigned
70
CITS : IT&ITES - Computer software application - Lesson 18 - 36