Page 111 - CITS - ED - Mechanical
P. 111
ENGINEERING DRAWING - CITS
EXERCISE 7 : Development and intersection
Development and intersection
Development of surfaces - Introduction
In our day-to-day life, we come across a number of objects. eg. Tins of round, square or rectangular shapes, fun-
nels, hoppers, ducts, chimneys, trunk boxes, machine guards, medicine cartons etc are made of sheets metals
and cardboards.
The process of manufacturing these objects involves cutting the flat sheet to the required size and then "folding
it" to the final shape. The term development refers to the size and shape of the unfolded sheet or sometimes
called as blanks. Development also implies the geometrical process of finding the size and shape of unfolded
sheet. Hence, the development of surface plays very important role, such that enabling a machine to cut proper
size of the sheet with reference to the development and to fold at proper places to obtain the required shape of
the objects, say boilers, boxes, buckets, chimneys, hoppers, ducts etc.
The development of surfaces can be defined as the unrolling or unfolding of all the surfaces of the
objects on a plane.
Types of surfaces
All objects are bounded by geometric surfaces, and so developments are made by the application of basic graphic
and geometric principles in co-ordination with mathematics. As different shapes has to be joined together in many
cases, the principle of intersections of solids are closely related to developments of surfaces.
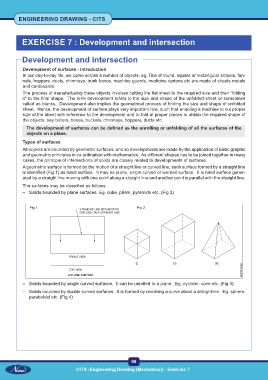
A geometric surface is formed by the motion of a straight line or curved line, such surface formed by a straight line
is identified (Fig 1) as ruled surface. It may be plane, single curved or warped surface. It is ruled surface gener-
ated by a straight line moving with one point along a straight line and another point is parallel with the straight line.
The surfaces may be classified as follows:
– Solids bounded by plane surfaces. Eg. cube, prism, pyramids etc. (Fig 2)
Fig 1 Fig 2
– Solids bounded by single curved surfaces. It can be unrolled to a plane. Eg. cylinder, cone etc. (Fig 3)
– Solids bounded by double curved surfaces. It is formed by revolving a curve about a straightline. Eg. sphere,
paraboloid etc. (Fig 4)
98
CITS :Engineering Drawing (Mechanical) - Exercise 7