Page 114 - CITS - ED - Mechanical
P. 114
ENGINEERING DRAWING - CITS
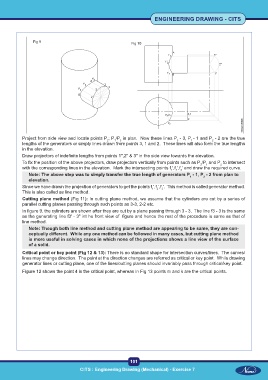
Fig 9 Fig 10
Project from side view and locate points P ; P /P in plan. Now these lines P - 3, P - 1 and P - 2 are the true
1
3
2
2
1
3
lengths of the generators or simply lines drawn from points 3, 1 and 2. These lines will also form the true lengths
in the elevation.
Draw projectors of indefinite lengths from points 1",2" & 3" in the side view towards the elevation.
To fix the position of the above projectors, draw projectors vertically from points such as P /P and P to intersect
1
3
2
with the corresponding lines in the elevation. Mark the intersecting points f ',f ',f ' and draw the required curve.
2
1
3
Note: The above step was to simply transfer the true length of generators P - 1, P - 2 from plan to
1
2
elevation.
Since we have drawn the projection of generators to get the points f ',f ',f '. This method is called generator method.
1
2
3
This is also called as line method.
Cutting plane method (Fig 11): In cutting plane method, we assume that the cylinders are cut by a series of
parallel cutting planes passing through such points as 3-3, 2-2 etc.
In figure 9, the cylinders are shown after they are cut by a plane passing through 3 - 3. The line f3 - 3 is the same
as the generating line f3' - 3" int he front view of figure and hence the rest of the procedure is same as that of
line method.
Note: Though both line method and cutting plane method are appearing to be same, they are con-
ceptually different. While any one method can be followed in many cases, but cutting plane method
is more useful in solving cases in which none of the projections shows a line view of the surface
of a solid.
Critical point or key point (Fig 12 & 13): There is no standard shape for intersection curves/lines. The curves/
lines may change direction. The point at the direction changes are referred as critical or key point. While drawing
generator lines or cutting plane, one of the lines/cutting planes should invariably pass through critical/key point.
Figure 12 shows the point 4 is the critical point, whereas in Fig 13 points m and k are the critical points.
101
CITS : Engineering Drawing (Mechanical) - Exercise 7