Page 226 - Electrician - TT (Volume 1)
P. 226
ELECTRICIAN - CITS
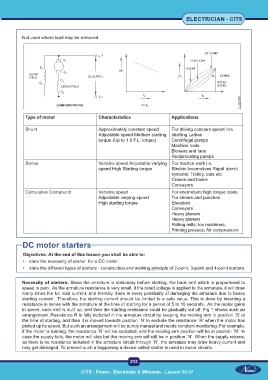
Not used where load may be removed
Type of motor Characteristics Applications
Shunt Approximately constant speed For driving constant speed line
Adjustable speed Medium starting shafting Lathes
torque (Up to 1.5 F.L. torque) Centrifugal pumps
Machine tools
Blowers and fans
Reciprocating pumps
Series Variable speed Adjustable variying For traction work i.e.
speed High Starting torque Electric locomotives Rapid transit
systems. Trolley, cars etc.
Cranes and hoists
Conveyors
Comulative Compound Variable speed For intermittent high torque loads
Adjustable varying speed For shears and punches
High starting torque Elevators
Conveyors
Heavy planers
Heavy planers
Rolling mills; Ice machines;
Printing presses; Air compressors
DC motor starters
Objectives: At the end of this lesson you shall be able to:
• state the necessity of starter for a DC motor
• state the different types of starters - construction and working principle of 2-point, 3-point and 4-point starters.
Necessity of starters: Since the armature is stationary before starting, the back emf which is proportional to
speed is zero. As the armature resistance is very small, if the rated voltage is applied to the armature, it will draw
many times the full load current, and thereby, there is every possibility of damaging the armature due to heavy
starting current. Therefore, the starting current should be limited to a safe value. This is done by inserting a
resistance in series with the armature at the time of starting for a period of 5 to 10 seconds. As the motor gains
in speed, back emf is built up, and then the starting resistance could be gradually cut off. Fig 1 shows such an
arrangement. Resistance R is fully included in the armature circuit by keeping the moving arm in position `S’ at
the time of starting, and then it is moved towards position `N’ to exclude the resistance `R’ when the motor has
picked up its speed. But such an arrangement will be purely manual and needs constant monitoring. For example,
if the motor is running, the resistance `R’ will be excluded, and the moving arm position will be at position `N’. In
case the supply fails, the motor will stop but the moving arm will still be in position `N’. When the supply returns,
as there is no resistance included in the armature circuit through `R’, the armature may draw heavy current and
may get damaged. To prevent such a happening a device called starter is used in motor circuits.
213
CITS : Power - Electrician & Wireman - Lesson 30-37 CITS : Power - Electrician & Wireman - Lesson 30-37