Page 230 - Electrician - TT (Volume 1)
P. 230
ELECTRICIAN - CITS
Constant losses
(1) Iron losses
(2) Mechanical losses
(3) Shunt field losses.
Variable losses
Armature copper loss (I a Ra)
2
Series field copper loss (I se R se).
2
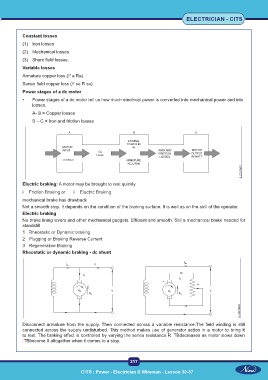
Power stages of a dc motor
• Power stages of a dc motor tell us how much electrical power is converted into mechanical power and into
losses.
A- B = Copper losses
B – C = Iron and friction losses
Electric braking: A motor may be brought to rest quickly
i Friction Braking or ii Electric Braking.
mechanical brake has drawback
Not a smooth stop. It depends on the condition of the braking surface. It is well as on the skill of the operator.
Electric braking
No brake lining levers and other mechanical gadgets. Efficient and smooth. Still a mechanical brake needed for
standstill
1 Rheostatic or Dynamic braking
2 Plugging or Braking Reverse Current
3 Regenerative Braking
Rheostatic or dynamic braking - dc shunt
Disconnect armature from the supply. Then connected across a variable resistance.The field winding is still
connected across the supply undisturbed. This method makes use of generator action in a motor to bring it
to rest. The braking effect is controlled by varying the series resistance R. TBdecreases as motor slows down
.TBbecome 0 altogether when it comes to a stop.
217
CITS : Power - Electrician & Wireman - Lesson 30-37 CITS : Power - Electrician & Wireman - Lesson 30-37