Page 231 - Electrician - TT (Volume 1)
P. 231
ELECTRICIAN - CITS
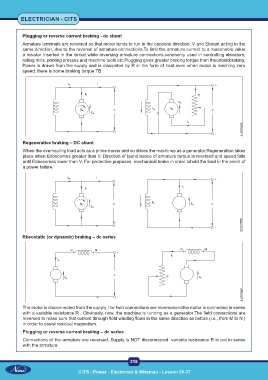
Plugging or reverse current braking - dc shunt
Armature terminals are reversed so that motor tends to run in the opposite direction. V and Ebstart acting in the
same direction, due to the reversal of armature connections.To limit the armature current to a reasonable value
a resistor inserted in the circuit while reversing armature connections.commonly used in controlling elevators,
rolling mills, printing presses and machine tools etc.Plugging gives greater braking torque than rheostaticbraking.
Power is drawn from the supply and is dissipated by R in the form of heat.even when motor is reaching zero
speed, there is some braking torque TB
Regenerative braking – DC shunt
When the overhauling load acts as a prime mover and so drives the machines as a generator.Regeneration takes
place when Ebbecomes greater than V. Direction of Iaand hence of armature torque is reversed and speed falls
until Ebbecomes lower than V. For protective purposes, mechanical brake in order tohold the load in the event of
a power failure.
Rheostatic (or dynamic) braking – dc series
The motor is disconnected from the supply, the field connections are reversedandthe motor is connected in series
with a variable resistance R . Obviously, now, the machine is running as a generator.The field connections are
reversed to make sure that current through field winding flows in the same direction as before (i.e., from M to N )
in order to assist residual magnetism.
Plugging or reverse current braking – dc series
Connections of the armature are reversed. Supply is NOT disconnected. variable resistance R is put in series
with the armature
218
CITS : Power - Electrician & Wireman - Lesson 30-37