Page 228 - Electrician - TT (Volume 1)
P. 228
ELECTRICIAN - CITS
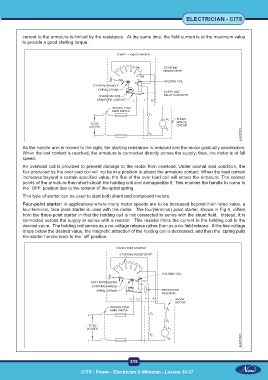
current to the armature is limited by the resistance. At the same time, the field current is at the maximum value
to provide a good starting torque.
As the handle arm is moved to the right, the starting resistance is reduced and the motor gradually accelerates.
When the last contact is reached, the armature is connected directly across the supply; thus, the motor is at full
speed.
An overload coil is provided to prevent damage to the motor from overload. Under normal load condition, the
flux produced by the over load coil will not be in a position to attract the armature contact. When the load current
increases beyond a certain specified value, the flux of the over load coil will attract the armature. The contact
points of the armature then short-circuit the holding coil and demagnetize it. This enables the handle to come to
the `OFF’ position due to the tension of the spiral spring.
This type of starter can be used to start both shunt and compound motors.
Four-point starter: In applications where many motor speeds are to be increased beyond their rated value, a
four-terminal, face plate starter is used with the motor. The four(terminal) point starter, shown in Fig 4, differs
from the three-point starter in that the holding coil is not connected in series with the shunt field. Instead, it is
connected across the supply in series with a resistor. This resistor limits the current in the holding coil to the
desired value. The holding coil serves as a no-voltage release rather than as a no-field release. If the line voltage
drops below the desired value, the magnetic attraction of the holding coil is decreased, and then the spring pulls
the starter handle back to the `off’ position.
215
CITS : Power - Electrician & Wireman - Lesson 30-37 CITS : Power - Electrician & Wireman - Lesson 30-37