Page 207 - Electrician - TT (Volume 2)
P. 207
ELECTRICIAN - CITS
• AC motors are better suited for high speed operation (over 2500 rpm) since there are no brushes, and
commutation is not a problem.
• Whenever the operating environment is wet, corrosive or explosive, special motor enclosures are required.
Special AC motor enclosure types are more readily available at lower prices.
• Multiple motors in a system must operate simultaneously at a common frequency/speed.
Disadvantages
• A standard motor can not adequately cool its winding at slow speed or handle the irregular electrical waveform
from the AC drive.
• An AC drive requires installation of motor with heavier windings.
• AC drive has complicated electronics circuit, so fault rectification is costly.
• AC drives produce a simulated waveform, not a perfect sine wave. That degrade the power equality.
Components of AC drive
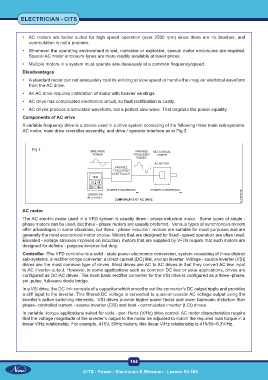
A variable frequency drive is a device used in a drive system consisting of the following three main sub-systems.
AC motor, main drive controller assembly, and drive / operator interface as in Fig 3.
Fig 3
AC motor
The AC electric motor used in a VFD system is usually three - phase induction motor. Some types of single -
phase motors can be used, but three - phase motors are usually preferred. Various types of synchronous motors
offer advantages in some situations, but three - phase induction motors are suitable for most purposes and are
generally the most economical motor choice. Motors that are designed for fixed - speed operation are often used.
Elevated - voltage stresses imposed on induction motors that are supplied by VFDs require that such motors are
designed for definite - purpose inverter-fed duty.
Controller :The VFD controller is a solid - state power electronics conversion, system consisting of three distinct
sub-systems, a rectifier bridge converter, a direct current (DC) link, and an inverter. Voltage - source inverter (VSI)
drives are the most common type of drives. Most drives are AC to AC drives in that they convert AC line input
to AC inverter output. However, in some applications such as common DC bus or solar applications, drives are
configured as DC-AC drives. The most basic rectifier converter for the VSI drive is configured as a three -phase,
six -pulse, full-wave diode bridge.
In a VSI drive, the DC link consists of a capacitor which smooths out the converter’s DC output ripple and provides
a stiff input to the inverter. This filtered DC voltage is converted to quasi-sinusoidal AC voltage output using the
inverter’s active switching elements. VSI drives provide higher power factor and lower harmonic distortion than
phase- controlled current - source inverter (CSI) and load - commutated inverter (LCI) drives.
In variable -torque applications suited for volts - per- Hertz (V/Hz) drive control. AC motor characteristics require
that the voltage magnitude of the inverter’s output to the motor be adjusted to match the required load torque in a
linear V/Hz relationship. For example, 415V, 50Hz motors, this linear V/Hz relationship is 415/50=8.3V/Hz.
194
CITS : Power - Electrician & Wireman - Lesson 93-100