Page 208 - Electrician - TT (Volume 2)
P. 208
ELECTRICIAN - CITS
Although space vector pulse- width modulation (SVPWM) is becoming increasingly popular, sinusoidal PWM
(SPWM) is the most straight forward method used to vary drives motor voltage ( or current) and frequency. With
SPWM control quasi- sinusoidal, variable - pulse-width output is constructed from intersections of a saw-toothed
carrier signal with a modulating sinusoidal signal which is variable in operating frequency as well as in voltage (or
current).
An embedded microprocessor governs the overall operation of the VFD controller. Basic programming of the
microprocessor is provided as user - inaccessible firmware. User programming of display, variable, and function
block parameters is provided to control, protect, and monitor the VFD, motor, and driven equipment.
Operator interface
The operator interface provides a means for an operator to start and stop the motor and adjust the operating
speed. Additional operator control functions might include reversing, and switching between manual speed
adjustment and automatic control from an external process control signal. The operator interface often includes
an alphanumeric display and /or indication lights and meters to provide information about the operation of the
drive.
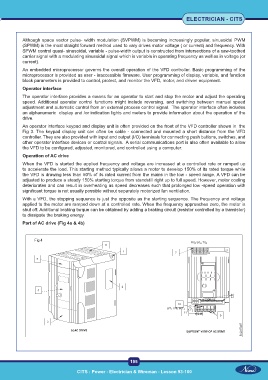
An operator interface keypad and display unit is often provided on the front of the VFD controller shown in the
Fig 3. The keypad display unit can often be cable - connected and mounted a short distance from the VFD
controller. They are also provided with input and output (I/O) terminals for connecting push buttons, switches, and
other operator interface devices or control signals. A serial communications port is also often available to allow
the VFD to be configured, adjusted, monitored, and controlled using a computer.
Operation of AC drive
When the VFD is started the applied frequency and voltage are increased at a controlled rate or ramped up
to accelerate the load. This starting method typically allows a motor to develop 150% of its rated torque while
the VFD is drawing less than 50% of its rated current from the mains in the low - speed range. A VFD can be
adjusted to produce a steady 150% starting torque from standstill right up to full speed. However, motor cooling
deteriorates and can result in overheating as speed decreases such that prolonged low -speed operation with
significant torque is not usually possible without separately motorized fan ventilation.
With a VFD, the stopping sequence is just the opposite as the starting sequence. The frequency and voltage
applied to the motor are ramped down at a controlled rate. When the frequency approaches zero, the motor is
shut off. Additional braking torque can be obtained by adding a braking circuit (resistor controlled by a transistor)
to dissipate the braking energy.
Part of AC drive (Fig 4a & 4b)
Fig 4
195
CITS : Power - Electrician & Wireman - Lesson 93-100 CITS : Power - Electrician & Wireman - Lesson 93-100