Page 215 - Electrician - TT (Volume 2)
P. 215
ELECTRICIAN - CITS
Types of AC voltage stabilizers
1 Stepped voltage stabilizer
a) Manual
b) Automatic relay type
2 Servo voltage stabilizer
3 Constant voltage transformer
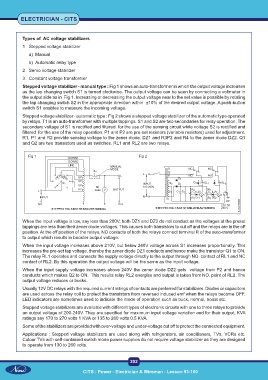
Stepped voltage stabilizer - manual type : Fig 1 shows an auto-transformer in which the output voltage increases
as the tap changing switch S1 is turned clockwise. The output voltage can be seen by connecting a voltmeter in
the output side as in Fig 1. Increasing or decreasing the output voltage near to the set value is possible by rotating
the tap changing switch S2 in the appropriate direction within ±10% of the desired output voltage. A push-button
switch S1 enables to measure the incoming voltage.
Stepped voltage stabilizer - automatic type : Fig 2 shows a stepped voltage stabilizer of the automatic type operated
by relays. T1 is an auto-transformer with multiple tappings. S1 and S2 are two secondaries for relay operation. The
secondary voltage of S1 is rectified and filtered for the use of the sensing circuit while voltage S2 is rectified and
filtered for the use of the relay operation. P1 and P2 are pre-set resistors (variable resistors) used for adjustment.
R1, P1 and R2 provide sensing voltage to the zener diode. DZ1 and R3P2 and R4 to the zener diode DZ2. Q1
and Q2 are two transistors used as switches. RL1 and RL2 are two relays.
Fig 1 Fig 2
When the input voltage is low, say less than 200V, both DZ1 and DZ2 do not conduct as the voltages at the preset
tappings are less than their zener diode voltages. This causes both transistors to cut off and the relays are in the off
position. At the off position of the relays, NO contacts of both the relays connect terminal R of the auto-transformer
to output which results in booster output voltage.
When the input voltage increases above 210V, but below 240V voltage across S1 increases proportionally. This
increases the pre-set tap voltage, thereby the zener diode DZ1 conducts and hence make the transistor Q1 to ON.
The relay RL1 operates and connects the supply voltage directly to the output through NO. contact of RL1 and NC
contact of RL2. By this operation the output voltage will be the same as the input voltage.
When the input supply voltage increases above 240V the zener diode DZ2 gets voltage from P2 and hence
conducts which makes Q2 to ON. This results relay RL2 energise and output is taken from NO. point of RL2. The
output voltage reduces or bucks.
Usually 12V DC relays with the required current ratings of contacts are preferred for stabilizers. Diodes or capacitors
are used across the relay coil to protect the transistors from reversed induced emf when the relays become OFF.
LED indicators are sometimes used to indicate the mode of operation such as buck, normal, boost etc.
Stepped voltage stabilizers are available with different types of electronic circuits with one to three relays to provide
an output voltage of 200-240V. They are specified for maximum input voltage variation and for their output, KVA
ratings say 170 to 270 volts 1 KVA or 135 to 260 volts 0.5 KVA.
Some of the stabilizers are provided with over-voltage and under-voltage cut off to protect the connected equipment.
Applications : Stepped voltage stabilizers are used along with refrigerators, air conditioners, TVs, VCRs etc.
Colour TVs with self-contained switch mode power supplies do not require voltage stabilizer as they are designed
to operate from 130 to 260 volts.
202
CITS : Power - Electrician & Wireman - Lesson 93-100