Page 46 - CITS - Electronic Mechanic - TT - 2024
P. 46
ELECTRONICS MECHANIC - CITS
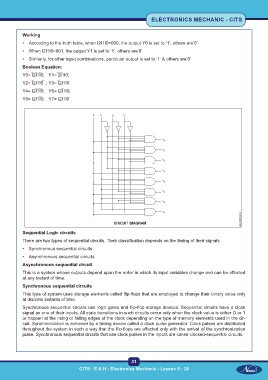
Working
• According to the truth table, when I2I1I0=000, the output Y0 is set to ‘1’, others are‘0’
• When I2I1I0=001, the output Y1 is set to ‘1’, others are‘0’
• Similarly, for other input combinations, particular output is set to ‘1’ & others are‘0’
Boolean Equation:
Y0= I̅2I̅1I̅0; Y1= ̅2I̅1I0;
Y2= I̅2I1I0̅ ; Y3= I̅2I1I0
Y4= I2I̅1I̅0; Y5= I2I̅1I0;
Y6= I2I1I̅0; Y7= I2I1I0
Sequential Logic circuits
There are two types of sequential circuits. Their classification depends on the timing of their signals
• Synchronous sequential circuits
• Asynchronous sequential circuits
Asynchronous sequential circuit
This is a system whose outputs depend upon the order in which its input variables change and can be affected
at any instant of time.
Synchronous sequential circuits
This type of system uses storage elements called flip-flops that are employed to change their binary value only
at discrete instants of time.
Synchronous sequential circuits use logic gates and flip-flop storage devices. Sequential circuits have a clock
signal as one of their inputs. All state transitions in such circuits occur only when the clock value is either O or 1
or happen at the rising or falling edges of the clock depending on the type of memory elements used in the cir-
cuit. Synchronization is achieved by a timing device called a clock pulse generator. Clock pulses are distributed
throughout the system in such a way that the flip-flops are affected only with the arrival of the synchronization
pulse. Synchronous sequential circuits that use clock pulses in the inputs are called clocked-sequential circuits.
31
CITS : E & H - Electronics Mechanic - Lesson 9 - 29