Page 33 - CITS - Fitter Trade Practical - Volume -2
P. 33
FITTER - CITS
• To resist corrosion or oxidation
• To obtain increased resistance to abrasion for wear resistance
• To obtain improved magnetic properties
• To refine grain size for high toughness.
Classification of alloy steels
• Low alloy – containing less than 5% of alloying elements
• Medium alloy – containing 5-10% of alloying elements
• High alloy – containing 10% or more of alloying elements.
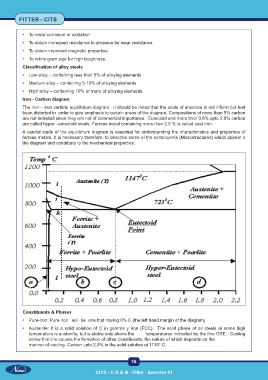
Iron - Carbon diagram
The iron – iron carbide equilibrium diagram. It should be noted that the scale of abscissa is not inform but had
been distorted in order to give emphasis to certain areas of the diagram. Compositions of more than 5% carbon
are not included since they are not of commercial importance. Eutectoid and more than 0.8% upto 2.0% carbon
are called hyper –eutectoid steels. Ferrous metal containing more than 2.0 % is called cast iron.
A careful study of the equilibrium diagram is essential for understanding the characteristics and properties of
ferrous metals. It is necessary therefore, to describe some of the constituents (Microstructures) which appear o
the diagram and contribute to the mechanical properties.
CITS : C G & M - Fitter - Exercise 59
Constituents & Phases
• Pure-iron: Pure iron will be one that having 0% C (the left hand margin of the diagram)
• Austenite: It is a solid solution of C in gamma y iron (FCC). The solid phase of all steels at some high
temperature is austenite, but is stable only above the temperatures indicated by the line GSE. Cooling
below this line causes the formation of other constituents, the nature of which depends on the
manner of cooling. Carbon upto 2.0% in the solid solution at 1130° C.
18
CITS : C G & M - Fitter - Exercise 61