Page 20 - Mechanic Diesel - TT
P. 20
MECHANIC DIESEL - CITS
Pareto principle was developed by Juran in 1950. A Pareto chart is a special type of histogram that can easily be
apply to find and prioritize quality problems, conditions, or their causes of in the organization (Juran and Godfrey,
1998). On the other hand, it is a type of bar chart that shows the relative importance of variables, prioritized in
descending order from left to right side of the chart. The aim of Pareto chart is to figure out the different kind of
“nonconformity” from data figures, maintenance data, repair data, parts scrap rates, or other sources. Also, Pareto
chart can generate a mean for investigating concerning quality improvement, and improving efficiency, “material
waste, energy conservation, safety issues, cost reductions”, etc., as Fig 4 demonstrated concerning Pareto chart,
it can able to improve the production before and after changes (Montgomery, 2009; Kerzner, 2009; Omachonu
and Ross, 2004).
Fig 4
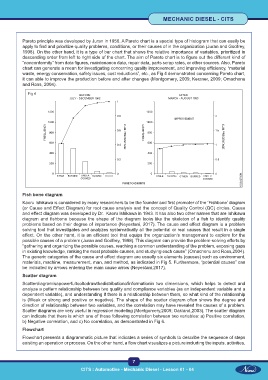
Fish bone diagram
Kaoru Ishikawa is considered by many researchers to be the founder and first promoter of the ‘Fishbone’ diagram
(or Cause and Effect Diagram) for root cause analysis and the concept of Quality Control (QC) circles. Cause
and effect diagram was developed by Dr. Kaoru Ishikawa in 1943. It has also two other names that are Ishikawa
diagram and fishbone because the shape of the diagram looks like the skeleton of a fish to identify quality
problems based on their degree of importance (Neyestani, 2017). The cause and effect diagram is a problem
solving tool that investigates and analyzes systematically all the potential or real causes that result in a single
effect. On the other hand, it is an efficient tool that equips the organization’s management to explore for the
possible causes of a problem (Juran and Godfrey, 1998). This diagram can provide the problem-solving efforts by
“gathering and organizing the possible causes, reaching a common understanding of the problem, exposing gaps
in existing knowledge, ranking the most probable causes, and studying each cause” (Omachonu and Ross,2004).
The generic categories of the cause and effect diagram are usually six elements (causes) such as environment,
materials, machine, measurement, man, and method, as indicated in Fig 5. Furthermore, “potential causes” can
be indicated by arrows entering the main cause arrow (Neyestani,2017).
Scatter diagram
Scatterdiagramisapowerfultooltodrawthedistributionofinformationin two dimensions, which helps to detect and
analyze a pattern relationship between two quality and compliance variables (as an independent variable and a
dependent variable), and understanding if there is a relationship between them, so what kind of the relationship
is (Weak or strong and positive or negative). The shape of the scatter diagram often shows the degree and
direction of relationship between two variables, and the correlation may have revealed the causes of a problem.
Scatter diagrams are very useful in regression modeling (Montgomery,2009; Oakland,2003). The scatter diagram
can indicate that there is which one of these following correlation between two variables: a) Positive correlation,
b) Negative correlation, and c) No correlation, as demonstrated in Fig 6.
Flowchart
Flowchart presents a diagrammatic picture that indicates a series of symbols to describe the sequence of steps
existing an operation or process. On the other hand, a flow chart visualizes a picture including the inputs, activities,
7
CITS : Automotive - Mechanic Diesel - Lesson 01 - 04