Page 272 - Mechanic Diesel - TT
P. 272
MECHANIC DIESEL - CITS
When the engine runs, a low pressure area is created in the intake manifold during the intake stroke of the piston.
It is used to open the filter valve, allowing fresh air to enter the bottom of the container. This air absorbs the fuel
vapor from here and comes to the inlet manifold and enters the combustion chamber of the engine and takes part
in combustion.
This filter valve is designed in such a way that it can operate at a speed higher than the idle speed of the engine.
If this valve operates at a low engine speed, excess fuel vapor will disturb the fuel air ratio, causing engine failure.
Evaporation of vehicle fuel is the main source of hydrocarbon emissions. The rate of evaporation of gasoline fuel
is higher than that of diesel because gasoline dissolves quickly.
Vehicle emission standard euro and bahrat standard, emission control
Introduction: In the automobile sector, pollutants are emitted into the atmosphere through the fuel tank, carburetor,
crack face and exhaust system. Fuel vapor is emitted from the fuel tank and carburetor, while the half-burned air-
fuel mixture is emitted from the crankcase between the piston and rings and the exhaust system emits half-burned
hydrocarbons, carbon monoxide, nitrogen oxides, and oxides of sulfur. are emitted. Apart from this, particulate
matter also plays a major role in exhaust emissions in diesel engines.
Apart from water, particulate fluid also includes those substances which are obtained by filtering the exhaust gas.
Some unburned hydrocarbons are absorbed above the smoke and carbon-containing particulate liquids.
Vehicle emissions standard: Every country sets standards for vehicle emissions. Standards related to vehicle
emissions have also been made by the Government of India. The Government of India has set some emission
standards, which are called ‘Bharat Stage Emission Standards’, to control the air pollution factors emitted from
the internal combustion of engines. The Central Pollution Control Board, under the leadership of the Ministry of
Environment and Forests, sets emission standards and sets deadlines. Every vehicle and machine should be
made as per the emission standards.
At present, the number of vehicles and machines is increasing day by day, as a result of which pollution in
the environment is also increasing. In order to control the pollution factors generated by vehicles, i.e. to avoid
pollution, the Central Pollution Board has set the values of various components in the fuel used in vehicles as
emission standards. Gas vacuum standards were first implemented in India in the year 1989, then instructions
were issued for petrol vehicles in the year 1991 and diesel vehicles in the year 1992. Bharat Stage III legislation
was passed in India since April, 2010, while Bharat Stage IV legislation was implemented in India since April,
2017.The Organization of European Countries unanimously passed the law of emission related standards for
all European countries in the year 2000, which is called Euro Stage Emission Standard. The details of emission
standards passed in India are as follows
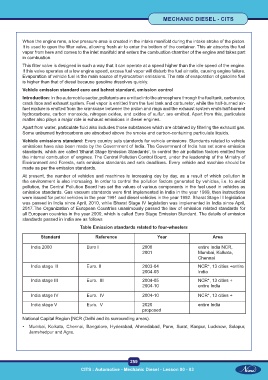
Table Emission standards related to four-wheelers
Standard Reference Year Area
India 2000 Euro I 2000 entire India NCR,
2001 Mumbai, Kolkata,
Chennai
India stage II Euro. II 2003-04 NCR*, 13 cities +entire
2004-05 India
India stage III Euro. III 2004-05 NCR*, 13 cities +
2004-10 entire India
India stage IV Euro. IV 2004-10 NCR*, 13 cities +
India stage V Euro. V 2020 entire India
proposed
National Capital Region [NCR (Delhi and its surrounding areas).
• Mumbai, Kolkata, Chennai, Bangalore, Hyderabad, Ahmedabad, Pune, Surat, Kanpur, Lucknow, Solapur,
Jamshedpur and Agra.
259
CITS : Automotive - Mechanic Diesel - Lesson 80 - 83