Page 276 - Mechanic Diesel - TT
P. 276
MECHANIC DIESEL - CITS
system. If the engine produces oxides of nitrogen, the EGR valve is opened, allowing some of the gases (6 to
10%) to pass through the exhaust and into the intake system. During combustion, these exhaust gases absorb
heat from the burning air and fuel. Due to this the combustion temperature decreases and nitrogen oxide is
formed by the reaction of nitrogen and oxygen. Older EGR systems use a vacuum regulated EGR valve while
newer vehicles use an electronic EGR valve to control the recirculation of exhaust gases.
When the engine operates at ideal conditions the EGR valve is kept closed. In this condition no EGR gas flows
from the manifold. The EGR valve is kept closed until the engine warms up and starts operating under load. As
load and combustion temperatures increase, the EGR valve is opened and exhaust gases begin to leak into
the manifold. This process produces a quenching effect which reduces the temperature of combustion thereby
reducing the formation of oxides of nitrogen.
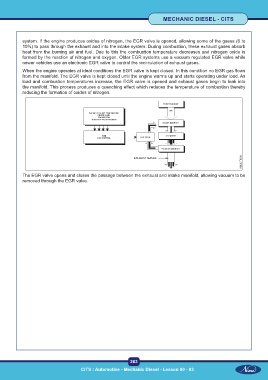
The EGR valve opens and closes the passage between the exhaust and intake manifold, allowing vacuum to be
removed through the EGR valve.
263
CITS : Automotive - Mechanic Diesel - Lesson 80 - 83