Page 275 - Mechanic Diesel - TT
P. 275
MECHANIC DIESEL - CITS
Devices for emissions control
In the beginning, when emission standards did not exist, there were no efforts towards emission control, but since
the emission standards came into existence, efforts have been made towards controlling the factors that pollute
the environment as a result of emissions. Efforts were also started and research was done keeping in mind the
emission control methods. The result of these researches came out in the form of emission control devices.
Following are some of those useful and popular emission control tips.
1 Catalytic conversation
A catalytic converter is an emissions control device that converts toxic pollutants into less toxic pollutants through
a redox catalytic reaction. Catalytic converter is mainly used in internal combustion engines.
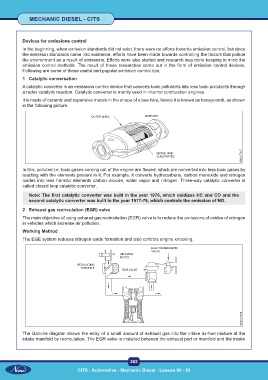
It is made of ceramic and expensive metals in the shape of a bee hive, hence it is known as honeycomb, as shown
in the following picture.
In this, polluted i.e. toxic gases coming out of the engine are flowed, which are converted into less toxic gases by
reacting with the elements present in it; For example, it converts hydrocarbons, carbon monoxide and nitrogen
oxides into less harmful elements carbon dioxide, water vapor and nitrogen. Three-way catalytic converter is
called closed loop catalytic converter.
Note: The first catalytic converter was built in the year 1976, which oxidizes HC and CO and the
second catalytic converter was built in the year 1977-78, which controls the emission of NO.
2 Exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) valve
The main objective of using exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) valve is to reduce the emissions of oxides of nitrogen
in vehicles which increase air pollution.
Working Method
The EGE system reduces nitrogen oxide formation and also controls engine knocking.
The Ganche diagram shows the entry of a small amount of exhaust gas into the intake air-fuel mixture at the
intake manifold by recirculation. The EGR valve is installed between the exhaust port or manifold and the intake
262
CITS : Automotive - Mechanic Diesel - Lesson 80 - 83