Page 140 - WCS - Electrical
P. 140
WORKSHOP CALCULATION & SCIENCE - CITS
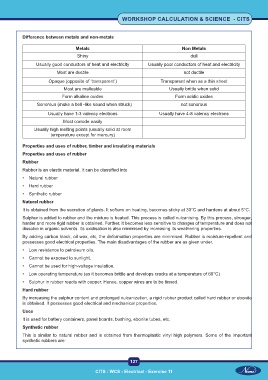
Difference between metals and non-metals
Metals Non Metals
Shiny dull
Usually good conductors of heat and electricity Usually poor conductors of heat and electricity
Most are ductile not ductile
Opaque (opposite of ‘transparent’) Transparent when as a thin sheet
Most are malleable Usually brittle when solid
Form alkaline oxides Form acidic oxides
Sonorous (make a bell -like sound when struck) not sonorous
Usually have 1-3 valency electrons Usually have 4-8 valency electrons
Most corrode easily
Usually high melting points (usually solid at room
temperature except for mercury)
Properties and uses of rubber, timber and insulating materials
Properties and uses of rubber
Rubber
Rubber is an elastic material. It can be classified into
• Natural rubber
• Hard rubber
• Synthetic rubber
Natural rubber
It is obtained from the secretion of plants. It softens on heating, becomes sticky at 30°C and hardens at about 5°C.
Sulphur is added to rubber and the mixture is heated. This process is called vulcanising. By this process, stronger,
harder and more rigid rubber is obtained. Further, it becomes less sensitive to changes of temperature and does not
dissolve in organic solvents. Its oxidisation is also minimised by increasing its weathering properties.
By adding carbon black, oil wax, etc, the deformation properties are minimised. Rubber is moisture-repellent and
possesses good electrical properties. The main disadvantages of the rubber are as given under.
• Low resistance to petroleum oils.
• Cannot be exposed to sunlight.
• Cannot be used for high-voltage insulation.
• Low operating temperature (as it becomes brittle and develops cracks at a temperature of 60°C)
• Sulphur in rubber reacts with copper. Hence, copper wires are to be tinned.
Hard rubber
By increasing the sulphur content and prolonged vulcanization, a rigid rubber product called hard rubber or ebonite
is obtained. It possesses good electrical and mechanical properties.
Uses
It is used for battery containers, panel boards, bushing, ebonite tubes, etc.
Synthetic rubber
This is similar to natural rubber and is obtained from thermoplastic vinyl high polymers. Some of the important
synthetic rubbers are:
127
CITS : WCS - Electrical - Exercise 11