Page 144 - WCS - Electrical
P. 144
WORKSHOP CALCULATION & SCIENCE - CITS
EXERCISE 12 : Heat & Temperature
Heat & Temperature
Introduction
- Heat and temperature are fundamental concepts in physics and thermodynamics.
- Although related, they represent distinct aspects of the thermal behavior of matter.
Heat
- Heat is one type of energy. Supply of heat to a body generally makes it hot and removal of heat makes it cold
- Heat energy can be transformed into other forms of energies..
- It flows spontaneously from a hotter body to a cooler body.
Temperature
- Temperature is a measure of the average kinetic energy of the particles in a substance.
- It determines the direction of heat flow and is measured using scales such as Celsius (°C), Fahrenheit (°F),
and Kelvin (K).
- Absolute zero (0 Kelvin) is the lowest possible temperature, where all molecular motion ceases.
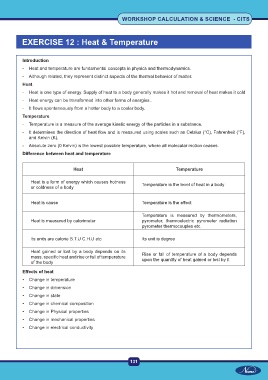
Difference between heat and temperature
Heat Temperature
Heat is a form of energy which causes hotness Temperature is the level of heat in a body
or coldness of a body
Heat is cause Temperature is the effect
Temperature is measured by thermometers,
Heat is measured by calorimeter pyrometer, thermoelectric pyrometer radiation
pyrometer thermocouples etc.
Its units are calorie B.T.U C.H.U etc Its unit is degree
Heat gained or lost by a body depends on its Rise or fall of temperature of a body depends
mass, specific heat and rise or fall of temperature upon the quantity of heat gained or lost by it
of the body
Effects of heat
• Change in temperature
• Change in dimension
• Change in state
• Change in chemical composition
• Change in Physical properties
• Change in mechanical properties
• Change in electrical conductivity
131