Page 115 - CITS - Welder - Trade Theory
P. 115
WELDER - CITS
d Basic or hydrogen-controlled electrodes: (Low hydrogen electrode e.g. E7018)
Basic or hydrogen controlled electrode coatings are based on calcium fluoride or calcium carbonate. This
type of electrode is suitable for welding high-strength steels without weld cracks and the coating have
to be dried. This drying is achieved by backing at 450°C holding at 300°C and storing at 150°C until
the time of use. By maintaining these conditions it is possible to achieve high strength weld deposits on
carbon, carbon manganese and low alloyed steels. Most electrodes in this group deposit welds with easily
removable slags, producing acceptable weld shape in all positions. Fumes given off by this electrode are
greater than with other types of electrodes.
Types of electrodes: Electric arc welding electrodes are of three general types. They are
a Carbon electrodes
b Bare electrodes
c Flux coated electrodes
a Carbon electrodes
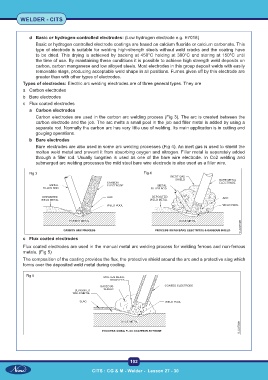
Carbon electrodes are used in the carbon arc welding process (Fig 3). The arc is created between the
carbon electrode and the job. The arc melts a small pool in the job and filler metal is added by using a
separate rod. Normally the carbon arc has very little use of welding. Its main application is in cutting and
gouging operations.
b Bare electrodes
Bare electrodes are also used in some arc welding processes (Fig 4). An inert gas is used to shield the
molten weld metal and prevent it from absorbing oxygen and nitrogen. Filler metal is separately added
through a filler rod. Usually tungsten is used as one of the bare wire electrode. In Co2 welding and
submerged arc welding processes the mild steel bare wire electrode is also used as a filler wire.
Fig 3 Fig 4
c Flux coated electrodes
Flux coated electrodes are used in the manual metal arc welding process for welding ferrous and non-ferrous
metals. (Fig 5)
The composition of the coating provides the flux, the protective shield around the arc and a protective slag which
forms over the deposited weld metal during cooling.
Fig 5
102
CITS : CG & M - Welder - Lesson 27 - 30