Page 118 - CITS - Welder - Trade Theory
P. 118
WELDER - CITS
e third digit indicating welding position(s) in which the electrode may be used and
f fourth digit indicating the current condition in which the electrode is to be used.
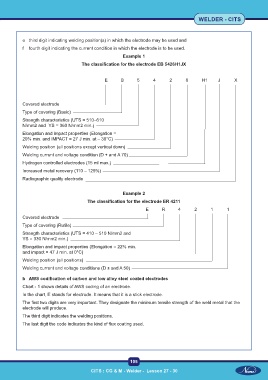
Example 1
The classification for the electrode EB 5426H1JX
E B 5 4 2 6 H1 J X
Covered electrode
Type of covering (Basic)
Strength characteristics (UTS = 510–610
N/mm2 and YS = 360 N/mm2 min.)
Elongation and impact properties (Elongation =
20% min. and IMPACT = 27 J min. at – 30°C)
Welding position (all positions except vertical down)
Welding current and voltage condition (D + and A 70)
Hydrogen controlled electrodes (15 ml max.)
Increased metal recovery (110 – 129%)
Radiographic quality electrode
Example 2
The classification for the electrode ER 4211
E R 4 2 1 1
Covered electrode
Type of covering (Rutile)
Strength characteristics (UTS = 410 – 510 N/mm2 and
YS = 330 N/mm2 min.)
Elongation and impact properties (Elongation = 22% min.
and impact = 47 J min. at 0°C)
Welding position (all positions)
Welding current and voltage conditions (D ± and A 50)
b AWS codification of carbon and low alloy steel coated electrodes
Chart - 1 shows details of AWS coding of an electrode.
In the chart, E stands for electrode. It means that it is a stick electrode.
The first two digits are very important. They designate the minimum tensile strength of the weld metal that the
electrode will produce.
The third digit indicates the welding positions.
The last digit the code indicates the kind of flux coating used.
105
CITS : CG & M - Welder - Lesson 27 - 30 CITS : CG & M - Welder - Lesson 27 - 30