Page 214 - CITS - Welder - Trade Theory
P. 214
WELDER - CITS
Plate First Pass Second Pass Third Pass
Thickness
T,mm
Electrode Dia Current Amps. Voltage Speed mm/sec Electrode Dia Current Amps mm Voltage Speed mm/sec Electrode Dia Mm Current amps . Voltage Speed mm/sec
32 5 850 35 V 5.5 5 1000 36 V 5 5 850 35 V 4
38 5 1000 36 4 5 1000 36 4 5 1000 34 3
Micro plasma welding principles, Equipment, power
source, parameter settings, Advantages
Objectives : At the end of this lesson you shall be able to
• describe the micro plasma welding
• explain the micro plasma equipments
• explain the micro plasma advantage.
Introduction
Micro plasma arc welding is welding process in which plasma producing gas (Argon, Nitrogen, Helium, and
Hydrogen) is ionized by the heat of an electric arc and passed through a small welding torch orifice. A shielding
gas protects the plasma arc from atmospheric contamination in welding or cutting. A non-consumable Tungsten
electrode is used in Plasma Arc Welding and additional metal is added to the weld with a filler rod.
Plasma Arc welding uses the keyhole method to obtain a full penetration and can be done manually or
automatically. The works of temperature obtained in this process is about 20000ºC to 30,000ºC.
It is divided in to two basic types. They are:
1 Transferred arc
2 Non-transferred arc
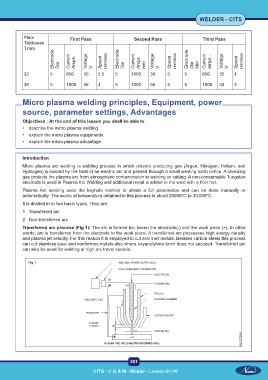
Transferred arc process (Fig 1): The arc is formed be- tween the electrode(-) and the work piece (+). In other
words, arc is transferred from the electrode to the work piece. A transferred arc possesses high energy density
and plasma jet velocity. For this reason it is employed to cut and melt metals. Besides carbon steels this process
can cut stainless steel and nonferrous metals also where oxyacetylene torch does not succeed. Transferred arc
can also be used for welding at high arc travel speeds.
Fig 1
201
CITS : C G & M - Welder - Lesson 61-76