Page 215 - CITS - Welder - Trade Theory
P. 215
WELDER - CITS
Fig 2
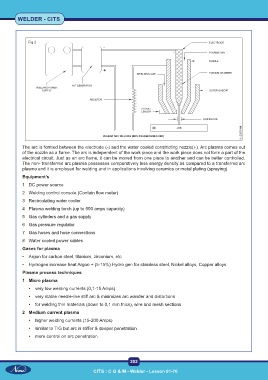
The arc is formed between the electrode (-) and the water cooled constricting nozzle(+). Arc plasma comes out
of the nozzle as a flame. The arc is independent of the work piece and the work piece does not form a part of the
electrical circuit. Just as an arc flame, it can be moved from one place to another and can be better controlled.
The non- transferred arc plasma possesses comparatively less energy density as compared to a transferred arc
plasma and it is employed for welding and in applications involving ceramics or metal plating (spraying).
Equipment’s
1 DC power source
2 Welding control console (Contain flow meter)
3 Recirculating water cooler
4 Plasma welding torch (up to 500 amps capacity)
5 Gas cylinders and a gas supply
6 Gas pressure regulator
7 Gas hoses and hose connections
8 Water cooled power cables
Gases for plasma
• Argon for carbon steel, titanium, zirconium, etc
• Hydrogen increase heat Argon + (5-15%) Hydro gen for stainless steel, Nickel alloys, Copper alloys
Plasma process techniques
1 Micro plasma
• very low welding currents (0,1-15 Amps)
• very stable needle-like stiff arc & minimizes arc wander and distortions
• for welding thin materials (down to 0,1 mm thick), wire and mesh sections
2 Medium current plasma
• higher welding currents (15-200 Amps)
• similar to TIG but arc is stiffer & deeper penetration
• more control on arc penetration.
202
CITS : C G & M - Welder - Lesson 61-76 CITS : C G & M - Welder - Lesson 61-76