Page 220 - CITS - Welder - Trade Theory
P. 220
WELDER - CITS
iii Cutting gas type and its flow rate. iv Distance between nozzle and job. v Cutting speed.
vi Plasma cutting current.
vii Power used during cutting. viii Manual/machine cutting.
ix Material to be cut and its thickness.
x Quality of cut required - rough or smooth. xi The bevel angle and round off corner etc.
Advantages of plasma cutting
i All metals and non-metals can be cut due to the high temperature and high velocity plasma flame.
ii Cuts are of very clear form with little or no dross. iii High speed piercing is achieved.
iv Cutting of piled plates is possible, even with different materials.
v Cutting cost is quite low as compared to other processes, especially for stainless steels.
vi Cutting speed is high.
vii Cutting is possible in all positions and locations (underwater also).
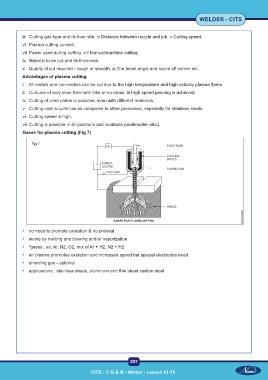
Gases for plasma cutting (Fig 7)
Fig 7
• no need to promote oxidation & no preheat
• works by melting and blowing and/or vaporization
• “gases : air, Ar, N2, O2, mix of Ar + H2, N2 + H2
• air plasma promotes oxidation and increased speed but special electrodes need
• shielding gas - optional
• applications : stainless steels, aluminum and thin sheet carbon steel.
207
CITS : C G & M - Welder - Lesson 61-76