Page 80 - CITS - Welder - Trade Theory
P. 80
WELDER - CITS
The process of making oxide is called oxidation. Oxygen is found everywhere in nature, either in free state or in a
combination with other elements. It is one of the chief constituents of atmosphere i.e., 21% oxygen 78% Nitrogen.
Water is chemical compound of oxygen and hydrogen, in which approximately 89% is oxygen by weight and 1/3
by volume. One volume of liquid oxygen produces 860 volumes of oxygen gas. One kg of liquid oxygen produces
750 liters of gas. The weight of the container used to store liquid oxygen is several times less than the weight of
cylinders required to store an equivalent quantity of gaseous oxygen.
Manufacturing method
Air liquefaction process:
This method is based upon the idea of separating the various gases that constitute the air by liquefaction process.
This process is done in three stages.
a purification
b liquefaction
c Distillation
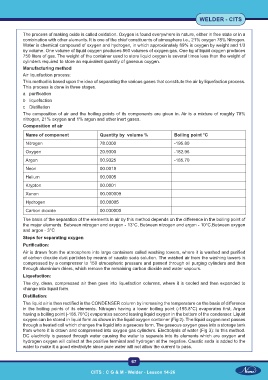
The composition of air and the boiling points of its components are given in. Air is a mixture of roughly 78%
nitrogen, 21% oxygen and 1% argon and other inert gases.
Composition of air
Name of component Quantity by volume % Boiling point °C
Nitrogen 78.0300 -195.80
Oxygen 20.9300 -182.96
Argon 00.9325 -185.70
Neon 00.0018
Helium 00.0005
Krypton 00.0001
Xenon 00.000009
Hydrogen 00.00005
Carbon dioxide 00.030000
The basis of the separation of the elements in air by this method depends on the difference in the boiling point of
the major elements. Between nitrogen and oxygen - 13°C, Between nitrogen and argon - 10°C,Between oxygen
and argon - 3°C
Steps for separating oxygen
Purification:
Air is drawn from the atmosphere into large containers called washing towers, where it is washed and purified
of carbon dioxide dust particles by means of caustic soda solution. The washed air from the washing towers is
compressed by a compressor to 150 atmospheric pressure and passed through oil purging cylinders and then
through aluminium driers, which remove the remaining carbon dioxide and water vapours.
Liquefaction:
The dry, clean, compressed air then goes into liquefaction columns, where it is cooled and then expanded to
change into liquid form.
Distillation:
The liquid air is then rectified in the CONDENSER column by increasing the temperature on the basis of difference
in the boiling points of its elements. Nitrogen having a lower boiling point (-195.8°C) evaporates first. Argon
having a boiling point (-185.70°C) evaporates second leaving liquid oxygen in the bottom of the condenser. Liquid
oxygen can be stored in liquid form as shown in the liquid oxygen container (Fig 2). The liquid oxygen next passes
through a heated coil which changes the liquid into a gaseous form. The gaseous oxygen goes into a storage tank
from where it is drawn and compressed into oxygen gas cylinders. Electrolysis of water (Fig 3): In this method.
DC electricity is passed through water causing the water to separate into its elements which are oxygen and
hydrogen oxygen will collect at the positive terminal and hydrogen at the negative. Caustic soda is added to the
water to make it a good electrolyte since pure water will not allow the current to pass.
67
CITS : C G & M - Welder - Lesson 14-26 CITS : C G & M - Welder - Lesson 14-26