Page 25 - CITS - ED - Mechanical
P. 25
ENGINEERING DRAWING - CITS
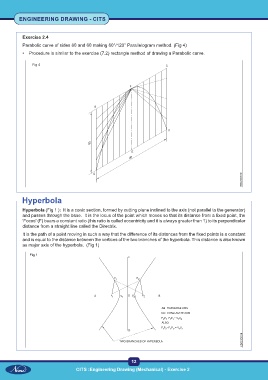
Exercise 2.4
Parabolic curve of sides 80 and 60 making 60°/120° Parallelogram method. (Fig 4)
• Procedure is similar to the exercise (7.2) rectangle method of drawing a Parabolic curve.
Fig 4
Hyperbola
Hyperbola (Fig 1 ): It is a conic section, formed by cutting plane inclined to the axis (not parallel to the generator)
and passes through the base. It is the locus of the point which moves so that its distance from a fixed point, the
'Focus' (F) bears a constant ratio (this ratio is called eccentricity and it is always greater than 1) to its perpendicular
distance from a straight line called the Directrix.
It is the path of a point moving in such a way that the difference of its distances from the fixed points is a constant
and is equal to the distance between the vertices of the two branches of the hyperbola. This distance is also known
as major axis of the hyperbola. (Fig 1)
Fig 1
12
CITS :Engineering Drawing (Mechanical) - Exercise 2