Page 268 - Electrician - TT (Volume 1)
P. 268
ELECTRICIAN - CITS
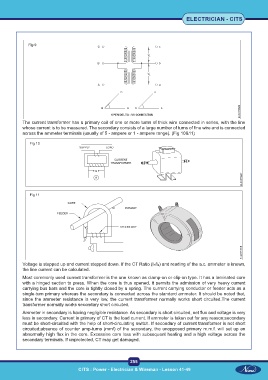
Fig 9
The current transformer has a primary coil of one or more turns of thick wire connected in series, with the line
whose current is to be measured. The secondary consists of a large number of turns of fine wire and is connected
across the ammeter terminals (usually of 5 - ampere or 1 - ampere range). (Fig 10&11)
Fig 10
Fig 11
Voltage is stepped up and current stepped down. If the CT Ratio (I1/I2) and reading of the a.c. ammeter is known,
the line current can be calculated.
Most commonly used current transformer is the one known as clamp-on or clip-on type. It has a laminated core
with a hinged section to press. When the core is thus opened, it permits the admission of very heavy current
carrying bus bars and the core is tightly closed by a spring. The current carrying conductor or feeder acts as a
single-turn primary whereas the secondary is connected across the standard ammeter. It should be noted that,
since the ammeter resistance is very low, the current transformer normally works short circuited.The current
transformer normally works secondary short circuited.
Ammeter in secondary is having negligible resistance. As secondary is short circuited, net flux and voltage is very
less in secondary. Current in primary of CT is the load current. If ammeter is taken out for any reason;secondary
must be short-circuited with the help of short-circulating switch. If secondary of current transformer is not short
circuited;absence of counter amp-turns (mmf) of the secondary, the unopposed primary m.m.f. will set up an
abnormally high flux in the core. Excessive core loss with subsequent heating and a high voltage across the
secondary terminals. If unprotected, CT may get damaged.
255
CITS : Power - Electrician & Wireman - Lesson 41-49 CITS : Power - Electrician & Wireman - Lesson 41-49