Page 77 - Electrician - TT (Volume 2)
P. 77
ELECTRICIAN - CITS
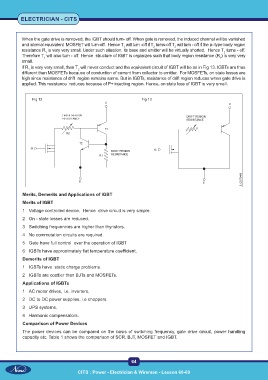
When the gate drive is removed, the IGBT should turn- off. When gate is removed, the induced channel will be vanished
and internal equivalent MOSFET will turn-off. Hence T will turn -off if T turns-off T will turn - off if the p- type body region
2
2
1
resistance R is very very small. Under such situation, its base and emitter will be virtually shorted. Hence T turns - off.
2
1
Therefore T will also turn - off. Hence structure of IGBT is organizes such that body region resistance (R ) is very very
1
1
small.
If R is very very small, than T will never conduct and the equivalent circuit of IGBT will be as in Fig 13. IGBTs are thus
2
1
different than MOSFETs because of conduction of current from collector to emitter. For MOSFETs, on state losses are
high since resistance of drift region remains same. But in IGBTs, resistance of drift region reduces when gate drive is
applied. This resistance reduces because of P+ injecting region. Hence, on state loss of IGBT is very small.
Fig 12 Fig 13
Merits, Demerits and Applications of IGBT
Merits of IGBT
1 Voltage controlled device. Hence drive circuit is very simple.
2 On - state losses are reduced.
3 Switching frequencies are higher than thyristors.
4 No commutation circuits are required.
5 Gate have full control over the operation of IGBT
6 IGBTs have approximately flat temperature coefficient.
Demerits of IGBT
1 IGBTs have static charge problems.
2 IGBTs are costlier than BJTs and MOSFETs.
Applications of IGBTs
1 AC motor drives, i.e. inverters.
2 DC to DC power supplies, i.e choppers
3 UPS systems.
4 Harmonic compensators.
Comparison of Power Devices
The power devices can be compared on the basis of switching frequency, gate drive circuit, power handling
capacity etc. Table 1 shows the comparison of SCR, BJT, MOSFET and IGBT.
64
CITS : Power - Electrician & Wireman - Lesson 60-69