Page 72 - Electrician - TT (Volume 2)
P. 72
ELECTRICIAN - CITS
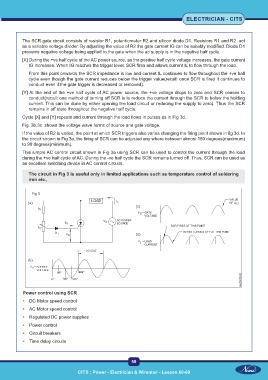
The SCR gate circuit consists of resistor R1, potentiometer R2 and silicon diode D1. Resistors R1 and R2 act
as a variable voltage divider. By adjusting the value of R2 the gate current IG can be suitably modified. Diode D1
prevents negative voltage being applied to the gate when the ac supply is in the negative half cycle.
[X] During the +ve half cycle of the AC power source, as the positive half cycle voltage increases, the gate current
IG increases. When IG reaches the trigger level, SCR fires and allows current IL to flow through the load.
From this point onwards the SCR impedance is low and current IL continues to flow throughout the +ve half
cycle even though the gate current reduces below the trigger value(recall: once SCR is fired it continues to
conduct even if the gate trigger is decreased or removed).
[Y] At the end of the +ve half cycle of AC power source, the +ve voltage drops to zero and SCR ceases to
conduct(recall: one method of turning off SCR is to reduce the current through the SCR to below the holding
current. This can be done by either opening the load circuit or reducing the supply to zero). Thus the SCR
remains in off state throughout the negative half cycle.
Cycle [X] and [Y] repeats and current through the load flows in pulses as in Fig 3d.
Fig 3b,3c shows the voltage wave forms of source and gate voltage.
If the value of R2 is varied, the point at which SCR triggers also varies changing the firing point shown in fig 3d. In
the circuit shown in Fig 3a, the firing of SCR can be adjusted any where between almost 180 degrees(maximum)
to 90 degrees(minimum).
This simple AC control circuit shown in Fig 3a using SCR can be used to control the current through the load
during the +ve half cycle of AC. During the -ve half cycle the SCR remains turned off. Thus, SCR can be used as
an excellent switching device in AC control circuits.
The circuit in Fig 3 is useful only in limited applications such as temperature control of soldering
iron etc.,
Fig 3
Power control using SCR
• DC Motor speed control
• AC Motor speed control
• Regulated DC power supplies
• Power control
• Circuit breakers
• Time delay circuits
59
CITS : Power - Electrician & Wireman - Lesson 60-69