Page 69 - Electrician - TT (Volume 2)
P. 69
ELECTRICIAN - CITS
While troubleshooting any electronic system, two main methods are generally adopted. They are:
Step-by-step method of troubleshooting: This approach is preferred by the beginners. In this approach, the
problem causing part or section is identified by testing the parts or sections from the beginning to the end as
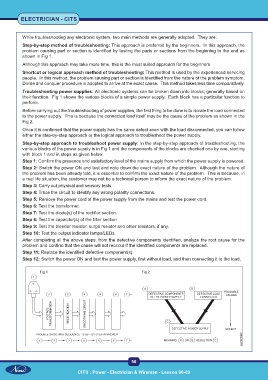
shown in Fig 1.
Although this approach may take more time, this is the most suited approach for the beginners.
Shortcut or logical approach method of troubleshooting: This method is used by the experienced servicing
people. In this method, the problem causing part or section is identified from the nature of the problem symptom.
Divide and conquer procedure is adopted to arrive at the exact cause. This method takes less time comparatively.
Troubleshooting power supplies: All electronic systems can be broken down into blocks, generally based on
their function. Fig 1 shows the various blocks of a simple power supply. Each block has a particular function to
perform.
Before carrying out the troubleshooting of power supplies, the first thing to be done is to isolate the load connected
to the power supply. This is because the connected load itself may be the cause of the problem as shown in the
Fig 2.
Once it is confirmed that the power supply has the same defect even with the load disconnected, you can follow
either the step-by-step approach or the logical approach to troubleshoot the power supply.
Step-by-step approach to troubleshoot power supply: In the step-by-step approach of troubleshooting, the
various blocks of the power supply is in Fig 1 and the components of the blocks are checked one by one, starting
with block 1 and in steps as given below.
Step 1: Confirm the presence and satisfactory level of the mains supply from which the power supply is powered.
Step 2: Switch the power ON and test and note down the exact nature of the problem. Although the nature of
the problem has been already told, it is essential to confirm the exact nature of the problem. This is because, in
a real life situation, the customer may not be a technical person to inform the exact nature of the problem.
Step 3: Carry out physical and sensory tests.
Step 4: Trace the circuit to identify any wrong polarity connections.
Step 5: Remove the power cord of the power supply from the mains and test the power cord.
Step 6: Test the transformer.
Step 7: Test the diode(s) of the rectifier section.
Step 8: Test the capacitor(s) of the filter section.
Step 9: Test the bleeder resistor, surge resistor and other resistors, if any.
Step 10: Test the output indicator lamps/LEDs.
After completing all the above steps, from the defective components identified, analyze the root cause for the
problem and confirm that the cause will not reoccur if the identified components are replaced.
Step 11: Replace the identified defective component(s).
Step 12: Switch the power ON and test the power supply, first without load, and then connecting it to the load.
Fig 1 Fig 2
56
CITS : Power - Electrician & Wireman - Lesson 60-69