Page 73 - Electrician - TT (Volume 2)
P. 73
ELECTRICIAN - CITS
• Soft start circuits
• Pulse, logic and digital circuits and so on.
Speed control of DC motors: In this Related Theory information only brief outline of power circuits is discussed.
Due variation of motor load currents, inductance effect in winding, the practical circuit should be modified to suit
the requirement. DC motors consists of field winding and armature winding. The speed of DC motors can be
varied by two methods,
1 controlling the field current
2 controlling the armature voltage
The first method is used for controlling the motor speed above the rated speed of the motor. The second method
is used for controlling the motor speed below the rated speed of the motor.
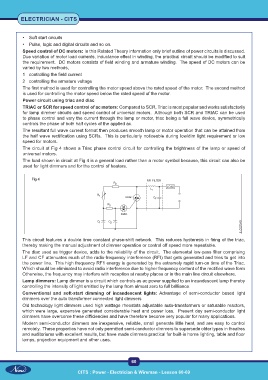
Power circuit using triac and diac
TRIAC or SCR for speed control of ac motors: Compared to SCR, Triac is most popular and works satisfactorily
for lamp dimmer circuits and speed control of universal motors. Although both SCR and TRIAC can be used
to phase control and vary the current through the lamp or motor, triac being a full wave device, symmetrically
controls the phase of both half cycles of the applied ac.
The resultant full wave current format then produces smooth lamp or motor operation that can be attained from
the half wave rectification using SCRs. This is particularly noticeable during low/dim light requirement or low
speed for motors.
The circuit at Fig 4 shows a Triac phase control circuit for controlling the brightness of the lamp or speed of
universal motors.
The load shown in circuit at Fig 4 is a general load rather than a motor symbol because, this circuit can also be
used for light dimmers and for the control of heaters.
Fig 4
This circuit features a double time constant phase-shift network. This reduces hysteresis in firing of the triac,
thereby making the manual adjustment of dimmer operation or control off speed more repeatable.
The diac used as trigger device, adds to the reliability of the circuit. The elemental low-pass filter comprising
LF and CF attenuates much of the radio-frequency interference (RFI) that gets generated and tries to get into
the power line. This high frequency RF1 energy is generated by the extremely rapid turn-on time of the Triac.
Which should be eliminated to avoid radio interference due to higher frequency content of the rectified wave form
Otherwise, the frequency may interfere with reception at nearby places or in the main line circuit elsewhere.
Lamp dimmers: Lamp dimmer is a circuit which controls as ac power supplied to an incandescent lamp thereby
controlling the intensity of light emitted by the lamp from almost zero to full brilliance.
Conventional and soft-start dimming of incandescent lights: Advantage of semi-conductor based light
dimmers over the auto transformer connected light dimmers
Old technology light dimmers used high wattage rheostats adjustable auto-transformers or saturable reactors,
which were large, expensive generated considerable heat and power loss. Present day semi-conductor light
dimmers have overcome these difficiencies and have therefore become very popular for many applications.
Modern semi-conductor dimmers are inexpensive, reliable, small generate little heat, and are easy to control
remotely. These properties have not only permitted semi-conductor dimmers to supersede older types in theatres
and auditoriums with excellent results, but have made dimmers practical for built-in home lighting, table and floor
lamps, projection equipment and other uses.
60
CITS : Power - Electrician & Wireman - Lesson 60-69