Page 64 - Electrician - TT (Volume 2)
P. 64
ELECTRICIAN - CITS
The frequency of oscillation
f =
Where RE is the value of variable resistor in ohms and C is the value of the capacitor in farad.
By varying the value of RE, the frequency of the oscillator can be varied. Although such an oscillator using a dc
supply voltage could be used to trigger a SCR, there would be trouble in synchronizing the pulses with the cycles
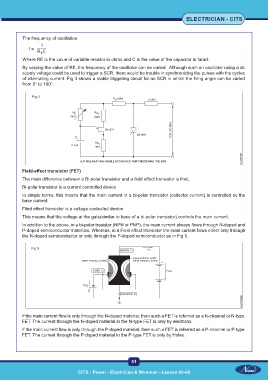
of alternating current. Fig 4 shows a stable triggering circuit for an SCR in which the firing angle can be varied
from 0° to 180°.
Fig 4
Field-effect transistor (FET)
The main difference between a Bi-polar transistor and a field effect transistor is that,
Bi-polar transistor is a current controlled device
In simple terms, this means that the main current in a bi-polar transistor (collector current) is controlled by the
base current.
Filed effect transistor is a voltage controlled device
This means that the voltage at the gate(similar to base of a bi-polar transistor) controls the main current.
In addition to the above, in a bi-polar trasistor (NPN or PNP), the main current always flows through N-doped and
P-doped semiconductor materials. Whereas, in a Field effect transistor the main current flows either only through
the N-doped semiconductor or only through the P-doped semiconductor as in Fig 5.
Fig 5
If the main current flow is only through the N-doped material, then such a FET is referred as a N-channel or N-type
FET. The current through the N-doped material in the N-type FET is only by electrons.
If the main current flow is only through the P-doped material, then such a FET is referred as a P-channel or P-type
FET. The current through the P-doped material in the P-type FET is only by Holes.
51
CITS : Power - Electrician & Wireman - Lesson 60-69