Page 45 - CITS - WCS - Mechanical
P. 45
WORKSHOP CALCULATION - CITS
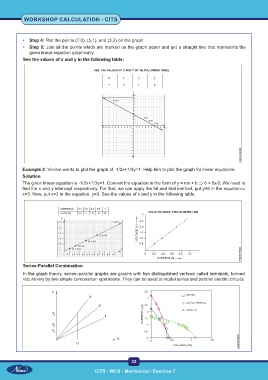
• Step 4: Plot the points (7,0), (5,1), and (3,2) on the graph.
• Step 5: Join all the points which are marked on the graph paper and get a straight line that represents the
given linear equation graphically.
See the values of x and y in the following table:
Example 2: Vikram wants to plot the graph of -1/2x+1/3y=1. Help him to plot the graph for linear equations.
Solution
The given linear equation is -1/2x+1/3y=1. Convert the equation in the form of y = mx + b ⇒ 6 + 6x/2. We need to
find the x and y-intercept respectively. For that, we can apply the hit and trial method, put y=6 in the equation⇒
x=3. Now, put x=2 in the equation. y=3. See the values of x and y in the following table.
Series-Parallel Combination
In the graph theory, series–parallel graphs are graphs with two distinguished vertices called terminals, formed
recursively by two simple composition operations. They can be used to model series and parallel electric circuits.
32
CITS : WCS - Mechanical - Exercise 7