Page 111 - CITS - Welder - Trade Practical
P. 111
WELDER - CITS
• Clean the joint and inspect for weld defects like porosity etc, and for slight root penetration and proper bonding.
• Prepare a copper and a brass tube as per dimension.
• Clean and remove the surface oxides by wire wool.
• Select the nozzle No. 5 and 1.6mmø silicon bronze filler rod.
• Apply flux to the filler rod.
• Set the oxidizing flame.
• Manipulate the blowpipe and filler rod with flux applied on it using proper angles to fill the bell mouthed groove.
• Clean and remove the flux residue.
• Inspect for external weld defects.
Skill Sequence
Brazing of square and lap joint on MS sheet of 2mm thick
Objectives: At the end of this exercise you shall be able to
• prepare and brazing of square and lap joint on MS sheet of 2mm thick.
Brazing of MS sheet (Job-1)
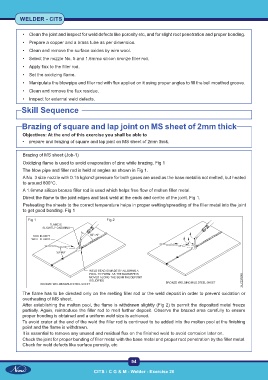
Oxidizing flame is used to avoid evaporation of zinc while brazing. Fig 1
The blow pipe and filler rod is held at angles as shown in Fig 1.
A No. 3 size nozzle with 0.15 kg/cm2 pressure for both gases are used as the base metal is not melted, but heated
to around 800°C.
A 1.6mmø silicon bronze filler rod is used which helps free flow of molten filler metal.
Direct the flame to the joint edges and tack weld at the ends and centre of the joint. Fig 1.
Preheating the sheets to the correct temperature helps in proper wetting/spreading of the filler metal into the joint
to get good bonding. Fig 1
Fig 1 Fig 2
Fig 1
The flame has to be directed only on the melting filler rod or the weld deposit in order to prevent oxidation or
overheating of MS sheet.
After establishing the molten pool, the flame is withdrawn slightly (Fig 2) to permit the deposited metal freeze
partially. Again, reintroduce the filler rod to melt further deposit. Observe the brazed area carefully to ensure
proper bonding is obtained and a uniform weld size is achieved.
To avoid crater at the end of the weld the filler rod is continued to be added into the molten pool at the finishing
point and the flame is withdrawn.
It is essential to remove any unused and residual flux on the finished weld to avoid corrosion later on.
Check the joint for proper bonding of filler metal with the base metal and proper root penetration by the filler metal.
Check for weld defects like surface porosity, etc.
94
CITS : C G & M - Welder - Exercise 20