Page 158 - CITS - Welder - Trade Theory
P. 158
WELDER - CITS
Constant voltage power source for CO welding- Working
2
principal, advantage & limitation of GMAW over other
welding process
Objectives: At the end of this lesson you shall be able to
• describe the GMAW power source
• explain the principal of power source GMAW
• explain the GMAW power source advantage.
Mig Welding Power Source
MIG welding power sources have come a long way from the basic transformer type power source to the highly
electronic and sophisticated types we see around today. Even though the technology of MIG welding has
changed, the principles of the MIG power source have, in most cases, not. The MIG power sources use mains
power and converts that mains power into CV (constant voltage), DC (direct current) power suitable for the MIG
welding process. MIG welding power sources control voltage – this is done by either voltage stepped switches,
wind handles, or electronically. The amperage that the power source produces is controlled by the cross sectional
area of the wire electrode and the wire speed, ie the higher the wire speed for each wire size, the higher the
amperage the power source will produce. Because the output of the MIG power source is DC (direct current) the
terminals on the front will have + positive and negative on the output side. The principles of electric circuits states
that 70% of the heat is always on the positive side.
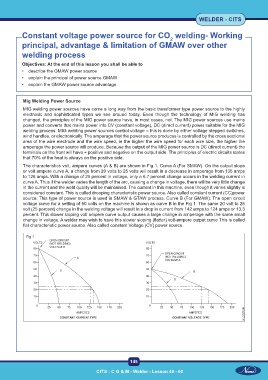
The characteristics volt, ampere curves (A & B) are shown in Fig 1. Curve A (For SMAW): On the output slope
or volt ampere curve A, a change from 20 volts to 25 volts will result in a decrease in amperage from 135 amps
to 126 amps. With a change of 25 percent in voltage, only a 6.7 percent change occurs in the welding current in
curve A. Thus if the welder varies the length of the arc, causing a change in voltage, there will be very little change
in the current and the weld quality will be maintained. The current in this machine, even though it varies slightly is
considered constant. This is called drooping characteristic power source. Also called constant current (CC)power
source. This type of power source is used in SMAW & GTAW process. Curve B (For GMAW): The open circuit
voltage curve for a setting of 50 volts on the machine is shown as curve B in the Fig 1. The same 20 volt to 25
volt (25 percent) change in the welding voltage will result in a drop in current from 142 amps to 124 amps or 13.3
percent. This slower sloping volt ampere curve output causes a large change in amperage with the same small
change in voltage. A welder may wish to have this slower sloping (flatter) volt-ampere output curve This is called
flat characteristic power source. Also called constant Voltage (CV) power source.
Fig 1
145
CITS : C G & M - Welder - Lesson 49 - 60