Page 160 - CITS - Welder - Trade Theory
P. 160
WELDER - CITS
iii Provides gas flow control through a solenoid valve. The gas is fed down from the gas regulator to the weld
area via the feeder and then the MIG welding torch.
Wire feeders come in many different shapes and sizes, but they all do the same basic job roles. Feeders can be
separated from the power source or built into the power source itself. Feeders are made up of different parts,
each having a different job role.
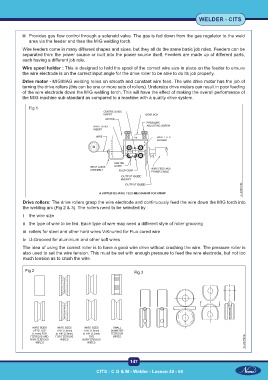
Wire spool holder : This is designed to hold the spool of the correct wire size in place on the feeder to ensure
the wire electrode is on the correct input angle for the drive roller to be able to do its job properly.
Drive motor - MIG/MAG welding relies on smooth and constant wire feed. The wire drive motor has the job of
turning the drive rollers (this can be one or more sets of rollers). Undersize drive motors can result in poor feeding
of the wire electrode down the MIG welding torch. This will have the effect of making the overall performance of
the MIG machine sub-standard as compared to a machine with a quality drive system.
Fig 1
Drive rollers: The drive rollers grasp the wire electrode and continuously feed the wire down the MIG torch into
the welding arc (Fig 2 & 3). The rollers need to be selected by :
i the wire size
ii the type of wire to be fed. Each type of wire may need a different style of roller grooving
iii rollers for steel and other hard wires V-Knurled for Flux cored wire
iv U-Grooved for aluminium and other soft wires
The idea of using the correct roller is to have a good wire drive without crushing the wire. The pressure roller is
also used to set the wire tension. This must be set with enough pressure to feed the wire electrode, but not too
much tension as to crush the wire.
Fig 2 Fig 3
147
CITS : C G & M - Welder - Lesson 49 - 60