Page 165 - CITS - Welder - Trade Theory
P. 165
WELDER - CITS
a Spray transfer: In spray transfer very fine droplets of the electrode wire are rapidly projected through the arc
from the end of the electrode to the workpiece. (Fig 1) Spray transfer requires high current density (28 to 32V).
To obtain a good spray mode of welding shielding gases containing a blend of argon is used. The spray method of
metal transfer can be used with most of the common welding wire electrodes (eg mild steel, aluminium, stainless
steel). The advantages of metal spray transfer are
a high deposition rates
b good travel speeds
c good looking weld appearance
d little weld spatter
e good weld fusion
f very good on heavy sections
g The disadvantages of the spray mode are
h higher capacity power source needed
i weld position is limited to flat and horizontal fillet
j the cost of using a more expensive mixed gas
k higher radiated heat is produced so extra protection is needed
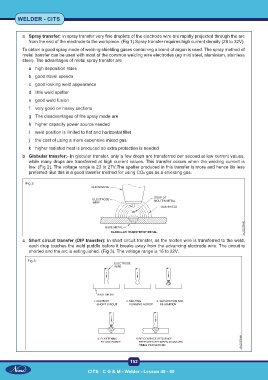
b Globular transfer:- In globular transfer, only a few drops are transferred per second at low current values,
while many drops are transferred at high current values. This transfer occurs when the welding current is
low. (Fig 2). The voltage range is 23 to 27V.The spatter produced in this transfer is more and hence itis less
preferred. But this is a good transfer method for using CO2 gas as a shielding gas.
Fig 2
c Short circuit transfer (DIP transfer): In short circuit transfer, as the molten wire is transferred to the weld,
each drop touches the weld puddle before it breaks away from the advancing electrode wire. The circuit is
shorted and the arc is extinguished. (Fig 3). The voltage range is 16 to 22V.
Fig 3
152
CITS : C G & M - Welder - Lesson 49 - 60