Page 191 - CITS - Welder - Trade Theory
P. 191
WELDER - CITS
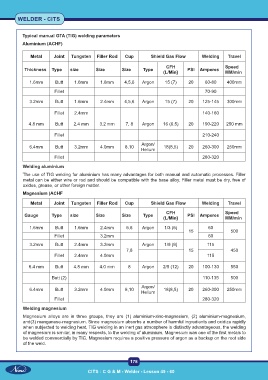
Typical manual GTA (TIG) welding parameters
Aluminium (ACHF)
Metal Joint Tungsten Filler Rod Cup Shield Gas Flow Welding Travel
CFH Speed
Thickness Type size Size Size Type (L/Min} PSI Amperes MM/min
1.6mm Butt 1.6mm 1.6mm 4,5,6 Argon 15 (7) 20 60-80 400mm
Fillet 70-90
3.2mm Butt 1.6mm 2.4mm 4,5,6 Argon 15 (7) 20 125-145 300mm
Fillet 2.4mm 140-160
4.8 mm Butt 2.4 mm 3.2 mm 7, 8 Argon 16 (6.5) 20 190-220 250 mm
Fillet 210-240
Argon/
6.4mm Butt 3.2mm 4.0mm 8,10 18(8,5) 20 260-300 250mm
Helium
Fillet 280-320
Welding aluminium
The use of TIG welding for aluminium has many advantages for both manual and automatic processes. Filler
metal can be either wire or rod and should be compatible with the base alloy. Filler metal must be dry, free of
oxides, grease, or other foreign matter.
Magnesium (ACHF
Metal Joint Tungsten Filler Rod Cup Shield Gas Flow Welding Travel
CFH Speed
Gauge Type size Size Size Type PSI Amperes
(L/Min} MM/min
1.6mm Butt 1.6mm 2.4mm 5,6 Argon 1/3 (5) 60
15 500
Fillet 3.2mm 60
3.2mm Butt 2.4mm 3.2mm Argon 1/9 (9) 115
7,8 15 450
Fillet 2.4mm 4.0mm 115
6.4 mm Butt 4.8 mm 4.0 mm 8 Argon 2/5 (12) 20 100-130 550
Butt (2) 110-135 500
Argon/
6.4mm Butt 3.2mm 4.0mm 8,10 18(8,5) 20 260-300 250mm
Helium
Fillet 280-320
Welding magnesium
Magnesium alloys are in three groups, they are (1) aluminium-zinc-magnesium, (2) aluminium-magnesium,
and(3) manganese-magnesium. Since magnesium absorbs a number of harmful ingredients and oxidize rapidly
when subjected to welding heat, TIG welding in an inert gas atmosphere is distinctly advantageous, the welding
of magnesium is similar, in many respects, to the welding of aluminium. Magnesium was one of the first metals to
be welded commercially by TIG. Magnesium requires a positive pressure of argon as a backup on the root side
of the weld.
178
CITS : C G & M - Welder - Lesson 49 - 60