Page 172 - CITS - ED - Mechanical
P. 172
ENGINEERING DRAWING - CITS
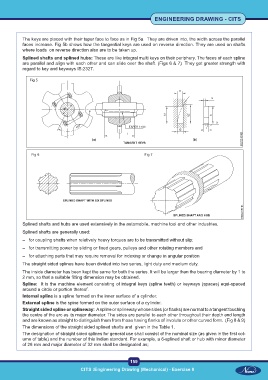
The keys are placed with their taper face to face as in Fig 5a. They are driven into, the width across the parallel
faces increase. Fig 5b shows how the tangential keys are used on reverse direction. They are used on shafts
where loads on reverse direction also are to be taken up.
Splined shafts and splined hubs: These are like integral multi keys on their periphery. The faces of each spline
are parallel and align with each other and can slide over the shaft. (Figs 6 & 7) They got greater strength with
regard to key and keyways IS:2327.
Fig 5
Fig 6 Fig 7
Splined shafts and hubs are used extensively in the automobile, machine tool and other industries.
Splined shafts are generally used:
– for coupling shafts when relatively heavy torques are to be transmitted without slip;
– for transmitting power by sliding or fixed gears, pulleys and other rotating members and
– for attaching parts that may require removal for indexing or change in angular position
The straight sided splines have been divided into two series, light duty and medium duty.
The inside diameter has been kept the same for both the series. It will be larger than the bearing diameter by 1 to
2 mm, so that a suitable fitting dimension may be obtained.
Spline: It is the machine element consisting of integral keys (spline teeth) or keyways (spaces) equi-spaced
around a circle or portion thereof.
Internal spline is a spline formed on the inner surface of a cylinder.
External spline is the spine formed on the outer surface of a cylinder.
Straight sided spline or splineway: A spline or splineway whose sides (or flanks) are normal to a tangent touching
the centre of the arc as its major diameter. The sides are parallel to each other throughout their depth and length
and are known as straight to distinguish them from those having flanks of involute or other curved form. (Fig 8 & 9)
The dimensions of the straight sided splined shafts and given in the Table 1.
The designation of straight sided splines for general use shall consist of the nominal size (as given in the first col-
umn of table) and the number of this Indian standard. For example, a 6-splined shaft or hub with minor diameter
of 28 mm and major diameter of 32 mm shall be designated as;
159
CITS :Engineering Drawing (Mechanical) - Exercise 8 CITS :Engineering Drawing (Mechanical) - Exercise 8