Page 228 - CITS - ED - Mechanical
P. 228
ENGINEERING DRAWING - CITS
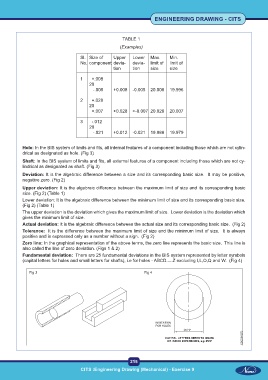
TABLE 1
(Examples)
Sl. Size of Upper Lower Max. Min.
No. component devia- devia- limit of limit of
tion tion size size
1 +.008
20
-.005 +0.008 -0.005 20.008 19.996
2 +.028
20
+.007 +0.028 +-0.007 20.028 20.007
3 -.012
20
-.021 +0.012 -0.021 19.988 19.979
Hole: In the BIS system of limits and fits, all internal features of a component including those which are not cylin-
drical as designated as hole. (Fig 3)
Shaft: In the BIS system of limits and fits, all external features of a component including those which are not cy-
lindrical as designated as shaft. (Fig 3)
Deviation: It is the algebraic difference between a size and its corresponding basic size. It may be positive,
negative zero. (Fig 2)
Upper deviation: It is the algebraic difference between the maximum limit of size and its corresponding basic
size. (Fig 2) (Table 1)
Lower deviation: It is the algebraic difference between the minimum limit of size and its corresponding basic size.
(Fig 2) (Table 1)
The upper deviation is the deviation which gives the maximum limit of size. Lower deviation is the deviation which
gives the minimum limit of size.
Actual deviation: It is the algebraic difference between the actual size and its corresponding basic size. (Fig 2)
Tolerance: It is the difference between the maximum limit of size and the minimum limit of size. It is always
positive and is expressed only as a number without a sign. (Fig 2)
Zero line: In the graphical representation of the above terms, the zero line represents the basic size. This line is
also called the line of zero deviation. (Figs 1 & 2)
Fundamental deviation: There are 25 fundamental deviations in the BIS system represented by letter symbols
(capital letters for holes and small letters for shafts), i.e for holes - ABCD.....Z excluding I,L,O,Q and W. (Fig 4)
Fig 3 Fig 4
215
CITS :Engineering Drawing (Mechanical) - Exercise 9 CITS :Engineering Drawing (Mechanical) - Exercise 9