Page 230 - Electrician - TT (Volume 2)
P. 230
ELECTRICIAN - CITS
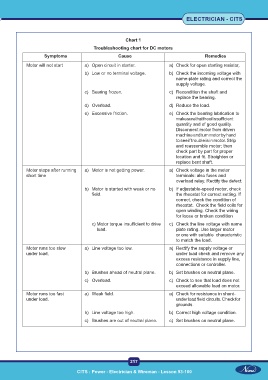
Chart 1
Troubleshooting chart for DC motors
Symptoms Cause Remedies
Motor will not start a) Open circuit in starter. a) Check for open starting resistor,
b) Low or no terminal voltage. b) Check the incoming voltage with
name-plate rating and correct the
supply voltage.
c) Bearing frozen. c) Recondition the shaft and
replace the bearing.
d) Overload. d) Reduce the load.
e) Excessive friction. e) Check the bearing lubrication to
make sure that the oil is sufficient
quantity and of good quality.
Disconnect motor from driven
machine and turn motor by hand
to see if trouble is in motor. Strip
and reassemble motor; then
check part by part for proper
location and fit. Straighten or
replace bent shaft.
Motor stops after running a) Motor is not getting power. a) Check voltage in the motor
short time terminals: also fuses and
overload relay. Rectify the defect.
b) Motor is started with weak or no b) If adjustable-speed motor, check
field. the rheostat for correct setting. If
correct, check the condition of
rheostat. Check the field coils for
open winding. Check the wiring
for loose or broken condition
c) Motor torque insufficient to drive c) Check the line voltage with name
load. plate rating. Use larger motor
or one with suitable characteristic
to match the load.
Motor runs too slow a) Line voltage too low. a) Rectify the supply voltage or
under load. under load check and remove any
excess resistance in supply line,
connections or controller.
b) Brushes ahead of neutral plane. b) Set brushes on neutral plane.
c) Overload. c) Check to see that load does not
exceed allowable load on motor.
Motor runs too fast a) Weak field. a) Check for resistance in shunt-
under load. under load field circuits. Check for
grounds.
b) Line voltage too high. b) Correct high voltage condition.
c) Brushes are out of neutral plane. c) Set brushes on neutral plane.
217
CITS : Power - Electrician & Wireman - Lesson 93-100 CITS : Power - Electrician & Wireman - Lesson 93-100