Page 126 - CITS - Welder - Trade Practical
P. 126
WELDER - CITS
Job Sequence
• Ensure the correct size of the pipes are used.
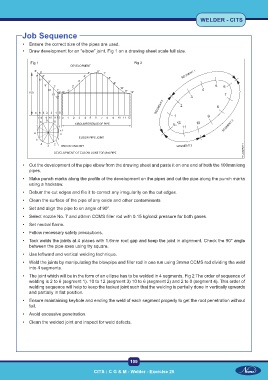
• Draw development for an “elbow” joint. Fig 1 on a drawing sheet scale full size.
Fig 1 Fig 2
• Cut the development of the pipe elbow from the drawing sheet and paste it on one end of both the 100mm long
pipes.
• Make punch marks along the profile of the development on the pipes and cut the pipe along the punch marks
using a hacksaw.
• Deburr the cut edges and file it to correct any irregularity on the cut edges.
• Clean the surface of the pipe of any oxide and other contaminants.
• Set and align the pipe to on angle of 90°.
• Select nozzle No. 7 and ø3mm CCMS filler rod with 0.15 kg/cm2 pressure for both gases.
• Set neutral flame.
• Follow necessary safety precautions.
• Tack welds the joints at 4 places with 1.6mm root gap and keep the joint in alignment. Check the 90° angle
between the pipe axes using try square.
• Use leftward and vertical welding technique.
• Weld the joints by manipulating the blowpipe and filler rod in one run using 3mmø CCMS rod dividing the weld
into 4 segments.
• The joint which will be in the form of an ellipse has to be welded in 4 segments. Fig 2 The order of sequence of
welding is 2 to 6 (segment 1). 10 to 12 (segment 3) 10 to 6 (segment 2) and 2 to 0 (segment 4). This order of
welding sequence will help to keep the tacked joint such that the welding is partially done in vertically upwards
and partially in flat position.
• Ensure maintaining keyhole and ending the weld of each segment properly to get the root penetration without
fail.
• Avoid excessive penetration.
• Clean the welded joint and inspect for weld defects.
109
CITS : C G & M - Welder - Exercise 25